使用TBE DSL进行算子开发,开发者只需要关注算子本身计算逻辑,无需关注调度策略,开发方式简单便捷。
目标
本节以add算子为例带您快速熟悉一个TBE DSL算子的编写流程。
Add算子实现了两个数据相加,返回相加结果的功能,如下所示:
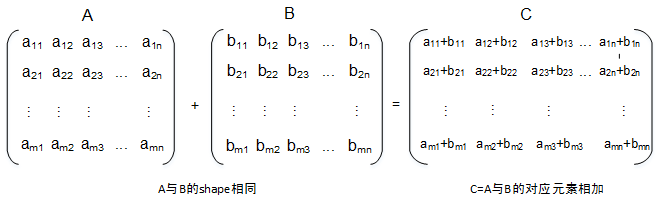
算子分析
使用TBE DSL方式开发Add算子前,需要确定算子功能、输入、输出,算子开发方式、算子类型以及算子实现函数名称等。
- 明确算子的功能以及数学表达式。
Add算子的数学表达式为:
y=x1+x2
计算过程是:将两个输入参数相加,得到最终结果z并将其返回。
- 明确输入和输出。
- Add算子有两个输入:x1与x2,输出为y。
- 本样例中算子的输入支持的数据类型为float16、float32、 int32,算子输出的数据类型与输入数据类型相同。
- 算子输入支持所有shape,输出shape与输入shape相同。
- 算子输入支持的format为:NCHW,NC1HWC0,NHWC,ND。
- 确定算子开发方式及使用的计算接口。
- 计算过程只涉及加法操作,查看TBE DSL API,初分析可使用tbe.dsl.vadd(lhs, rhs)接口实现x+y。
- 由于tbe.dsl.vadd(lhs, rhs)接口要求两个输入tensor的shape需要相同,所以需要首先获取两个输入tensor中较大的shape值,然后调用tbe.dsl.broadcast(var, shape, output_dtype=None)接口将入参广播成指定的shape大小。
- 明确算子实现文件名称、算子实现函数名称以及算子的类型(OpType)。
- 算子类型需要采用大驼峰的命名方式,即采用大写字符区分不同的语义。
- 算子实现文件名称和算子定义函数名称,可选用以下任意一种命名规则:
因此本例中,算子类型定义为Add;算子的实现文件名称及实现函数名称定义为add。
通过以上分析,得到Add算子的设计规格如下:
表1 Add算子设计规格 算子类型(OpType)
Add
算子输入
name:x1
shape:all
data type:
float16、float32、 int32
format:
NCHW,NC1HWC0,
NHWC,ND
name:x2
shape:all
data type:
float16、float32、 int32
format:
NCHW,NC1HWC0,
NHWC,ND
算子输出
name:y
shape:all
data type:
float16、float32、 int32
format:
NCHW,NC1HWC0,
NHWC,ND
算子实现使用主要DSL接口
tbe.dsl.broadcast(var, shape, output_dtype=None)
tbe.dsl.vadd(lhs, rhs)
算子实现文件/实现函数名称
add
算子代码实现
Add算子仅支持float16, float32, int32三种数据类型,所以需要对算子的输入数据进行校验;由于Add算子允许两个输入数据的shape不同,但算子计算接口tbe.dsl.vadd( )要求两输入shape相同,因此需要对算子两个输入的shape进行广播并对其进行校验,算子实现代码示例如下所示:
import tbe
from tbe import tvm
from tbe import dsl
from tbe.common.utils import para_check
from tbe.common.utils import shape_util
from functools import reduce
SHAPE_SIZE_LIMIT = 2147483648
# 实现Add算子的计算逻辑
@tbe.common.register.register_op_compute("add",op_mode="static")
def add_compute(input_x, input_y, output_z, kernel_name="add"):
shape_x = shape_util.shape_to_list(input_x.shape) # 将shape转换为list
shape_y = shape_util.shape_to_list(input_y.shape) # 将shape转换为list
shape_x, shape_y, shape_max = shape_util.broadcast_shapes(shape_x, shape_y,param_name_input1="input_x",param_name_input2="input_y") # shape_max取shape_x与shape_y的每个维度的大值
shape_size = reduce(lambda x, y: x * y, shape_max[:])
if shape_size > SHAPE_SIZE_LIMIT:
raise RuntimeError("the shape is too large to calculate")
input_x = dsl.broadcast(input_x, shape_max) # 将input_x的shape广播为shape_max
input_y = dsl.broadcast(input_y, shape_max) # 将input_y的shape广播为shape_max
res = dsl.vadd(input_x, input_y) # 执行input_x + input_y
return res # 返回计算结果的tensor
# 算子定义函数
def add(input_x, input_y, output_z, kernel_name="add"):
# 获取算子输入tensor的shape与dtype
shape_x = input_x.get("shape")
shape_y = input_y.get("shape")
check_tuple = ("float16", "float32", "int32")
input_data_type = input_x.get("dtype").lower()
if input_data_type not in check_tuple:
raise RuntimeError("only support %s while dtype is %s" %
(",".join(check_tuple), input_data_type))
# shape_max取shape_x与shape_y的每个维度的最大值
shape_x, shape_y, shape_max = shape_util.broadcast_shapes(shape_x, shape_y,param_name_input1="input_x",param_name_input2="input_y")
if shape_x[-1] == 1 and shape_y[-1] == 1 and shape_max[-1] == 1:
# 如果shape的长度等于1,就直接赋值,如果shape的长度不等于1,做切片,将最后一个维度舍弃(按照内存排布,最后一个维度为1与没有最后一个维度的数据排布相同,例如2*3=2*3*1,将最后一个为1的维度舍弃,可提升后续的调度效率)。
shape_x = shape_x if len(shape_x) == 1 else shape_x[:-1]
shape_y = shape_y if len(shape_y) == 1 else shape_y[:-1]
shape_max = shape_max if len(shape_max) == 1 else shape_max[:-1]
# 使用TVM的placeholder接口对第一个输入tensor进行占位,返回一个tensor对象
data_x = tvm.placeholder(shape_x, name="data_1", dtype=input_data_type)
# 使用TVM的placeholder接口对第二个输入tensor进行占位,返回一个tensor对象
data_y = tvm.placeholder(shape_y, name="data_2", dtype=input_data_type)
# 调用compute实现函数
res = add_compute(data_x, data_y, output_z, kernel_name)
# 自动调度
with tvm.target.cce():
schedule = dsl.auto_schedule(res)
# 编译配置
config = {"name": kernel_name,
"tensor_list": (data_x, data_y, res)}
dsl.build(schedule, config)
算子编译验证
- 在算子python文件最下方添加main函数调用该算子,代码示例如下所示:
1 2 3 4
# 算子调用 if __name__ == '__main__': input_output_dict = {"shape": (5, 6, 7),"format": "ND","ori_shape": (5, 6, 7),"ori_format": "ND", "dtype": "float16"} add(input_output_dict, input_output_dict, input_output_dict, kernel_name="add")
- 执行如下命令对算子实现文件进行编译,对实现代码进行语法校验。
python3 add.py
如果编译没有报错,且在当前目录下生成kernel_meta文件夹,包括以下文件,则表示算子代码能够编译运行。- 算子二进制文件add.o。
- 算子描述文件add.json:用于定义算子属性及运行时所需要的资源。