batch场景
单次Matmul计算处理的shape比较小时,由于每次计算均涉及到内部的通信,可能会影响性能,该接口提供批量处理Matmul的功能,调用一次IterateBatch,可以计算出多个singleCoreM * singleCoreN大小的C矩阵。
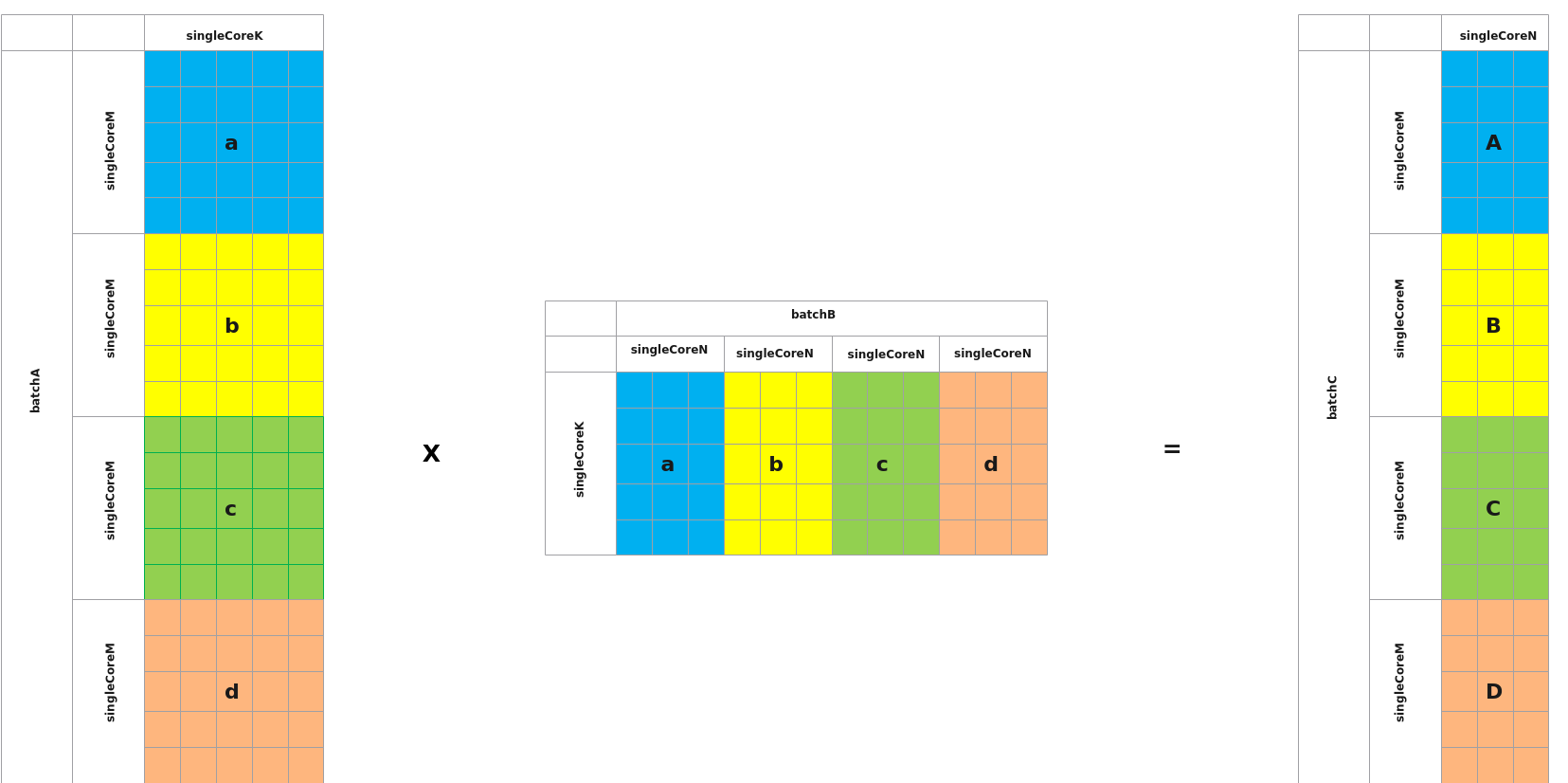
如下的示例中,包含4个矩阵乘操作a*a、b*b、c*c、d*d,需要单核上计算多个singleCoreM *singleCoreN,shape较小的情况可以使能BatchMatmul,批量处理。以BMK*BKN=BMN(相关格式参见IterateBatch)场景为例,如下图,一次IterateBatch可同时计算出A = a*a、B = b*b、C = c*c、D = d*d。
实例化Matmul时,需要通过MatmulType设置输入输出的Layout格式为NORMAL(BMNK的数据排布格式使用NORMAL表示)。Host侧Tiling时需使用SetBatchInfoForNormal设置A/B/C的M/N/K轴信息和A/B矩阵的BatchNum数。
如下示例完成aGM、bGM矩阵乘,结果保存到cGm上,其中aGM、bGM、cGM数据的layout格式均为NORMAL,左矩阵每次计算batchA个MK数据,右矩阵每次计算batchB个KN数据。更多详细示例请参考LINK,阅读该详细代码示例前,请参考LINK中的说明,选择与本手册配套的代码版本。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
#include "kernel_operator.h" #include "lib/matmul_intf.h" extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void kernel_matmul_rpc_batch(GM_ADDR aGM, GM_ADDR bGM, GM_ADDR cGM, GM_ADDR biasGM, GM_ADDR tilingGM, GM_ADDR workspaceGM, uint32_t isTransposeAIn, uint32_t isTransposeBIn, int32_t batchA, int32_t batchB) { // 定义matmul type typedef matmul::MatmulType <AscendC::TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, half, false, LayoutMode::NORMAL> aType; typedef matmul::MatmulType <AscendC::TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, half, true, LayoutMode::NORMAL> bType; typedef matmul::MatmulType <AscendC::TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, float, false, LayoutMode::NORMAL> cType; typedef matmul::MatmulType <AscendC::TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, float> biasType; // 初始化tiling数据 TCubeTiling tiling; auto tempTilingGM = (__gm__ uint32_t*)tilingGM; auto tempTiling = (uint32_t*)&tiling; for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(TCubeTiling) / sizeof(int32_t); ++i, ++tempTilingGM, ++tempTiling) { *tempTiling = *tempTilingGM; } // 初始化gm数据 AscendC::GlobalTensor<half> aGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<half> bGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<float> cGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<float> biasGlobal; int32_t sizeA = tiling.ALayoutInfoB * tiling.singleCoreM * tiling.singleCoreK * sizeof(A_T); int32_t sizeB = tiling.BLayoutInfoB * tiling.singleCoreK * tiling.singleCoreN * sizeof(B_T); int32_t sizeC = tiling.CLayoutInfoB * tiling.singleCoreM * tiling.singleCoreN * sizeof(C_T); int32_t sizebias = tiling.CLayoutInfoB * tiling.singleCoreN * sizeof(C_T); aGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ half*>(aGM), sizeA); bGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ half*>(bGM), sizeB); cGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ float*>(cGM), sizeC); biasGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ float*>(biasGM), sizebias); tiling.shareMode = 0; tiling.shareL1Size = 512 * 1024; tiling.shareL0CSize = 128 * 1024; tiling.shareUbSize = 0; int offset_a=0, offset_b=0, offset_c=0, offset_bias=0; AscendC::GlobalTensor<A_T> gm_a; gm_a.SetGlobalBuffer(const_cast<__gm__ A_T*>(aGlobal[offset_a].GetPhyAddr()), tiling.singleCoreM * tiling.singleCoreK); AscendC::GlobalTensor<B_T> gm_b; gm_b.SetGlobalBuffer(const_cast<__gm__ B_T*>(bGlobal[offset_b].GetPhyAddr()), tiling.singleCoreK * tiling.singleCoreN); AscendC::GlobalTensor<C_T> gm_c; gm_c.SetGlobalBuffer(const_cast<__gm__ C_T*>(cGlobal[offset_c].GetPhyAddr()), tiling.singleCoreM * tiling.singleCoreN) ; AscendC::GlobalTensor<BiasT> gm_bias; gm_bias.SetGlobalBuffer(const_cast<__gm__ BiasT*>(biasGlobal[offset_bias].GetPhyAddr()), tiling.singleCoreN); // 创建Matmul实例 constexpr MatmulConfig MM_CFG = GetNormalConfig(false, false, false, BatchMode::BATCH_LESS_THAN_L1); matmul::Matmul<aType, bType, cType, biasType, MM_CFG> mm1; AscendC::TPipe pipe; g_cubeTPipePtr = &pipe; SetSysWorkspace(workspaceGM); REGIST_MATMUL_OBJ(&pipe, GetSysWorkSpacePtr(), mm1); mm1.Init(&tiling); mm1.SetTensorA(gm_a, isTransposeAIn); mm1.SetTensorB(gm_b, isTransposeBIn); if(tiling.isBias) { mm1.SetBias(gm_bias); } // 多batch Matmul计算 mm1.IterateBatch(gm_c, batchA, batchB, false); } |
父主题: 矩阵编程(高阶API)