WelfordUpdate
功能说明
Welford是一种在线计算均值和方差的方法。一方面,它可以在不存储所有样本的情况下,逐步计算所有样本的均值和方差,更适合处理海量数据;另一方面,它只需要对数据进行一次遍历,能减少访存次数,提高计算性能。本接口为Welford算法的前处理。
LayerNorm算法中reduce轴较大的场景,可以通过切分reduce轴,联合使用本接口与WelfordFinalize,能够实现等效计算LayerNorm。本接口的计算公式如下:
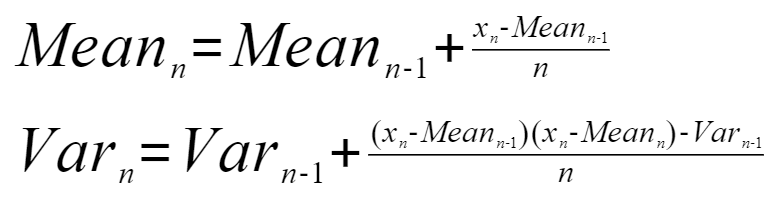
其中,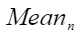 和
和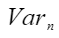 分别代表n个数据的均值和方差,
分别代表n个数据的均值和方差,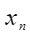 表示第n个点的数值。
表示第n个点的数值。
函数原型
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入临时空间
- 均值和方差的数据类型不固定
1 2
template <typename T, typename U,bool isReuseSource = false, const WelfordUpdateConfig& config = WFUPDATE_DEFAULT_CFG> __aicore__ inline void WelfordUpdate(const LocalTensor<U>& outputMean, const LocalTensor<U>& outputVariance, const LocalTensor<U>& inputMean, const LocalTensor<U>& inputVariance, const LocalTensor<T>& inputX, const LocalTensor<uint8_t>& sharedTmpBuffer, const WelfordUpdateParam& para)
- 均值和方差的数据类型不固定
- 接口框架申请临时空间
- 均值和方差的数据类型不固定
1 2
template <typename T, typename U,bool isReuseSource = false, const WelfordUpdateConfig& config = WFUPDATE_DEFAULT_CFG> __aicore__ inline void WelfordUpdate(const LocalTensor<U>& outputMean, const LocalTensor<U>& outputVariance, const LocalTensor<U>& inputMean, const LocalTensor<U>& inputVariance, const LocalTensor<T>& inputX, const WelfordUpdateParam& para)
- 均值和方差的数据类型不固定
由于该接口的内部实现中涉及复杂的计算,需要额外的临时空间来存储计算过程中的中间变量。临时空间支持接口框架申请和开发者通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入两种方式。
- 接口框架申请临时空间,开发者无需申请,但是需要预留临时空间的大小。
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入,使用该tensor作为临时空间进行处理,接口框架不再申请。该方式开发者可以自行管理sharedTmpBuffer内存空间,并在接口调用完成后,复用该部分内存,内存不会反复申请释放,灵活性较高,内存利用率也较高。
接口框架申请的方式,开发者需要预留临时空间;通过sharedTmpBuffer传入的情况,开发者需要为tensor申请空间。临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方式如下:通过WelfordUpdate Tiling中提供的GetWelfordUpdateMaxMinTmpSize接口获取所需最大和最小临时空间大小,最小空间可以保证功能正确,最大空间用于提升性能。
参数说明
参数名 |
描述 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
T |
inputX操作数的数据类型。 |
||||
U |
outputMean、outputVariance、inputMean、inputVariance操作数的数据类型。 |
||||
isReuseSource |
是否允许修改源操作数,默认值为false。如果开发者允许源操作数被改写,可以使能该参数,使能后能够节省部分内存空间。 设置为true,则本接口内部计算时复用inputX的内存空间,节省内存空间;设置为false,则本接口内部计算时不复用inputX的内存空间。 在 isReuseSource的使用样例请参考更多样例。 |
||||
config |
配置非指定计算范围内的目的操作数与源操作数的复用关系。WelfordUpdateConfig类型,定义如下:
配置示例如下:
此参数一般用于配合kernel侧tiling计算的接口使用。 |
参数名 |
输入/输出 |
描述 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
outputMean |
输出 |
均值目的操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 shape和源操作数inputMean需要保持一致。 |
||
outputVariance |
输出 |
方差目的操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 shape和源操作数inputVariance需要保持一致。 |
||
inputMean |
输入 |
均值源操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 |
||
inputVariance |
输入 |
方差源操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 |
||
inputX |
输入 |
源操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 |
||
sharedTmpBuffer |
输入 |
临时空间。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 接口内部复杂计算时用于存储中间变量,由开发者提供。 临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方式请参考WelfordUpdate Tiling。 |
||
para |
输入 |
计算所需的参数信息。WelfordUpdateParam类型,定义如下。
各目的操作数和源操作数的shape均为[rnLength, abLength]。 |
返回值
无
支持的型号
注意事项
- 接口参数para.rnLength当前只支持取值为1;
- 接口参数para.abLength的取值必须为32/sizeof(T)的整数倍;
- 接口参数para.abComputeLength的取值必须大于0。
调用示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 | #include "kernel_operator.h" constexpr AscendC::WelfordUpdateConfig WELFORD_UPDATE_ENABLE_INPLACE_CFG = { true }; constexpr AscendC::WelfordUpdateConfig WELFORD_UPDATE_UNENABLE_INPLACE_CFG = { false }; template <typename dataType, typename dataTypeU, bool isInplace = false> class KernelWelfordUpdate { public: __aicore__ inline KernelWelfordUpdate() {} __aicore__ inline void Init(GM_ADDR inputX_gm, GM_ADDR inputmean_gm, GM_ADDR inputvar_gm, GM_ADDR outputMean_gm, GM_ADDR outputVariance_gm, uint32_t nLength, uint32_t rLength, uint32_t abComputeLength) { this->nLength = nLength; this->rLength = rLength; this->abComputeLength = abComputeLength; totalLength = nLength * rLength; inputX_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ dataType *>(inputX_gm), totalLength); inputmean_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ dataTypeU *>(inputmean_gm), totalLength); inputvar_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ dataTypeU *>(inputvar_gm), totalLength); outputMean_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ dataTypeU *>(outputMean_gm), totalLength); outputVariance_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ dataTypeU *>(outputVariance_gm), totalLength); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueX, 1, sizeof(dataType) * totalLength); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueMean, 1, sizeof(dataTypeU) * totalLength); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueVar, 1, sizeof(dataTypeU) * totalLength); pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueMean, 1, sizeof(dataTypeU) * totalLength); pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueVariance, 1, sizeof(dataTypeU) * totalLength); } __aicore__ inline void Process() { CopyIn(); Compute(); CopyOut(); } private: __aicore__ inline void CopyIn() { AscendC::LocalTensor<dataType> inputXLocal = inQueueX.AllocTensor<dataType>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataTypeU> inmeanLocal = inQueueMean.AllocTensor<dataTypeU>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataTypeU> invarLocal = inQueueVar.AllocTensor<dataTypeU>(); AscendC::DataCopy(inputXLocal, inputX_global, totalLength); AscendC::DataCopy(inmeanLocal, inputmean_global, totalLength); AscendC::DataCopy(invarLocal, inputvar_global, totalLength); inQueueX.EnQue(inputXLocal); inQueueMean.EnQue(inmeanLocal); inQueueVar.EnQue(invarLocal); } __aicore__ inline void Compute() { AscendC::LocalTensor<dataType> inputXLocal = inQueueX.DeQue<dataType>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataTypeU> inmeanLocal = inQueueMean.DeQue<dataTypeU>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataTypeU> invarLocal = inQueueVar.DeQue<dataTypeU>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataTypeU> meanLocal = outQueueMean.AllocTensor<dataTypeU>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataTypeU> varianceLocal = outQueueVariance.AllocTensor<dataTypeU>(); struct AscendC::WelfordUpdateParam para = { nLength, rLength, abComputeLength, 0.3 }; if constexpr (isInplace) { AscendC::WelfordUpdate<dataType, dataTypeU, false, WELFORD_UPDATE_ENABLE_INPLACE_CFG>(meanLocal, varianceLocal, inmeanLocal, invarLocal, inputXLocal, para); } else { AscendC::WelfordUpdate<dataType, dataTypeU, false, WELFORD_UPDATE_UNENABLE_INPLACE_CFG>(meanLocal, varianceLocal, inmeanLocal, invarLocal, inputXLocal, para); } outQueueMean.EnQue<dataTypeU>(meanLocal); outQueueVariance.EnQue<dataTypeU>(varianceLocal); inQueueX.FreeTensor(inputXLocal); inQueueMean.FreeTensor(inmeanLocal); inQueueVar.FreeTensor(invarLocal); } __aicore__ inline void CopyOut() { AscendC::LocalTensor<dataTypeU> meanLocal = outQueueMean.DeQue<dataTypeU>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataTypeU> varianceLocal = outQueueVariance.DeQue<dataTypeU>(); AscendC::DataCopy(outputMean_global, meanLocal, totalLength); AscendC::DataCopy(outputVariance_global, varianceLocal, totalLength); outQueueMean.FreeTensor(meanLocal); outQueueVariance.FreeTensor(varianceLocal); } private: AscendC::GlobalTensor<dataType> inputX_global; AscendC::GlobalTensor<dataTypeU> inputmean_global; AscendC::GlobalTensor<dataTypeU> inputvar_global; AscendC::GlobalTensor<dataTypeU> outputMean_global; AscendC::GlobalTensor<dataTypeU> outputVariance_global; AscendC::TPipe pipe; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueX; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueMean; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueVar; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> outQueueMean; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> outQueueVariance; uint32_t nLength; uint32_t rLength; uint32_t abComputeLength; uint32_t totalLength; }; |