AscendDequant
功能说明
按元素做反量化计算,比如将int32_t数据类型反量化为half/float等数据类型。本接口最多支持输入为二维数据,不支持更高维度的输入。
- 假设输入srcTensor的shape为(m, n),每行数据(即n个输入数据)所占字节数要求32字节对齐,每行中进行反量化的元素个数为calCount;
- 反量化系数deqScale可以为标量或者向量,为向量的情况下,calCount <= deqScale的元素个数,只有前CalCount个反量化系数生效;
- 输出dstTensor的shape为(m, n_dst), n * sizeof(dstT)不满足32字节对齐时,需要向上补齐为32字节,n_dst为向上补齐后的列数。
下面通过两个具体的示例来解释参数的配置和计算逻辑(下文中DequantParams类型为存储shape信息的结构体{m, n, calCount}):
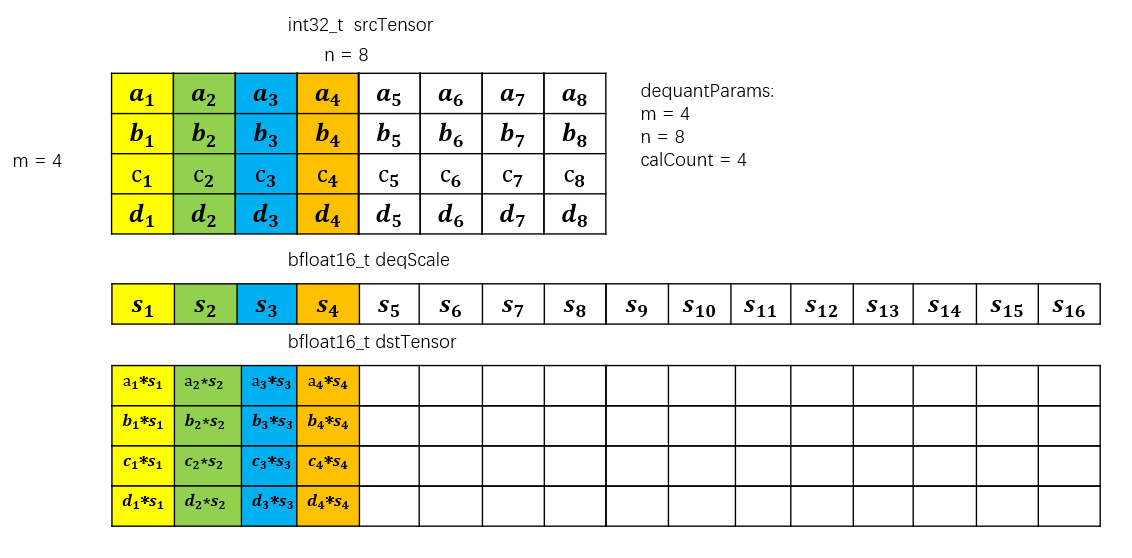
- 如下图示例中,srcTensor的数据类型为int32_t,m = 4,n = 8,calCount = 4,表明srcTensor中每行进行反量化的元素个数为4,deqScale中的前4个数生效,后12个数不参与反量化计算;dstTensor的数据类型为bfloat16_t,m = 4,n_dst = 16 (16 * sizeof(bfloat16_t) % 32 = 0)。计算逻辑是srcTensor的每n个数为一行,对于每行中的前calCount个元素,该行srcTensor的第i个元素与deqScale的第i个元素进行相乘写入dstTensor对应行的第i个元素,dstTensor对应行的第calCount + 1个元素~第n_dst个元素均为不确定的值。
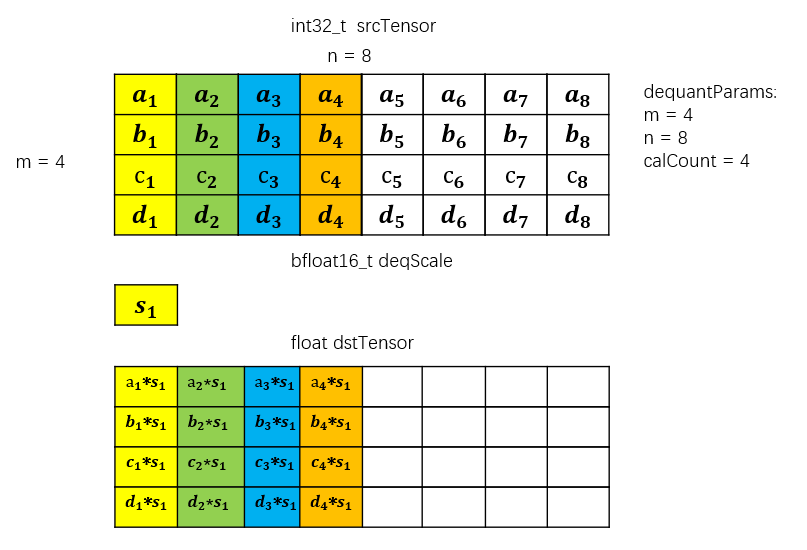
- 如下示例中,srcTensor的数据类型为int32_t,m = 4,n = 8, calCount = 4,表明srcTensor中每行进行反量化的元素个数为4;dstTensor的数据类型为float,m = 4,n_dst = 8 (8 * sizeof(float) % 32 = 0)。对于srcTensor每行中的前4个元素都和标量deqScale相乘并写入dstTensor中每行的对应位置。
当用户将模板参数中的mode配置为DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW时:
针对DequantParams {m, n, calCount}, 若同时满足以下3个条件:
- m = 1
- calCount为 32 / sizeof(dstT)的倍数
- n % calCount = 0
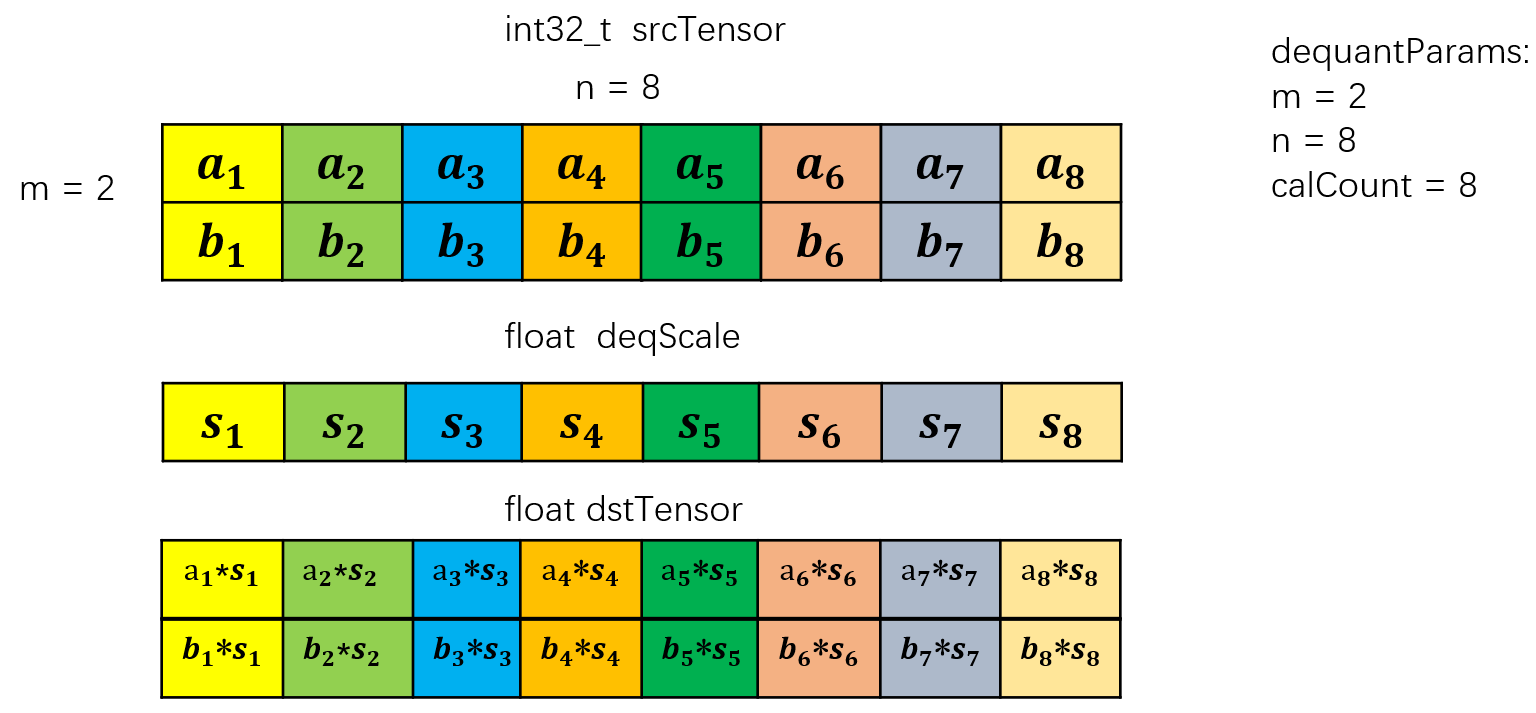
此时 {1, n, calCount}会被视作为 {n / calCount, calCount, calCount} 进行反量化的计算。
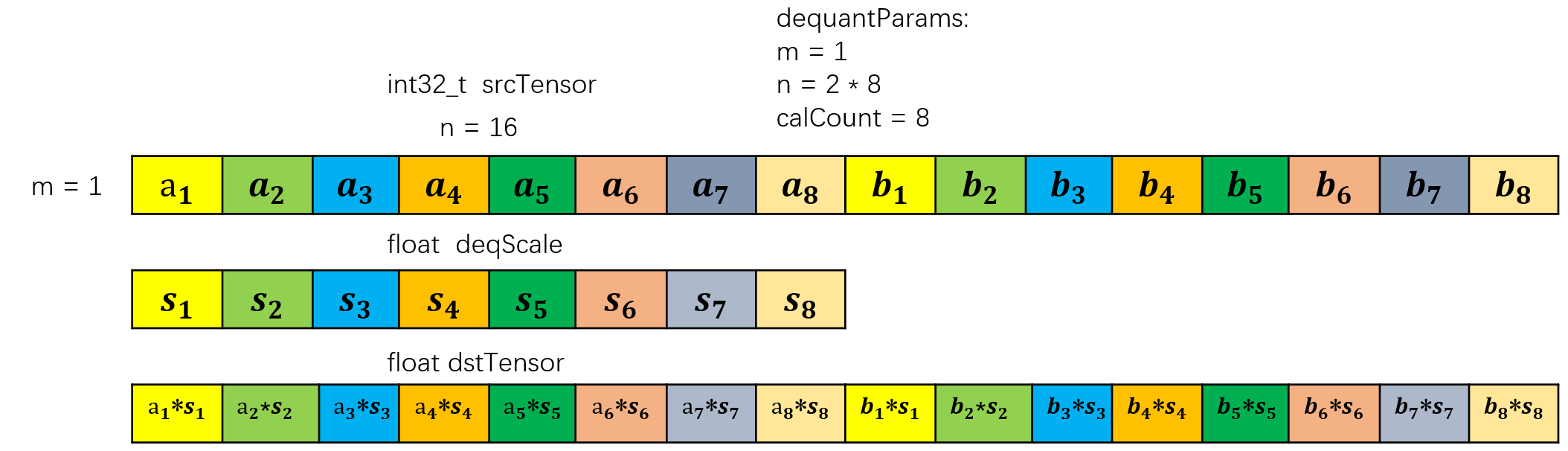
具体效果可看下图所示,传入的DequantParams为 {1, 16, 8}。因为dstT为float,所以calCount满足为8的倍数,在DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW模式下会将{1, 2 * 8, 8}转换为 {2, 8, 8}进行计算。
实现原理
以数据类型int32_t,shape为[m, n]的输入srcTensor,数据类型scaleT,shape为[n]的输入deqScale和数据类型dstT,shape为[m, n]的输出dstTensor为例,描述AscendDequant高阶API内部算法框图,如下图所示。
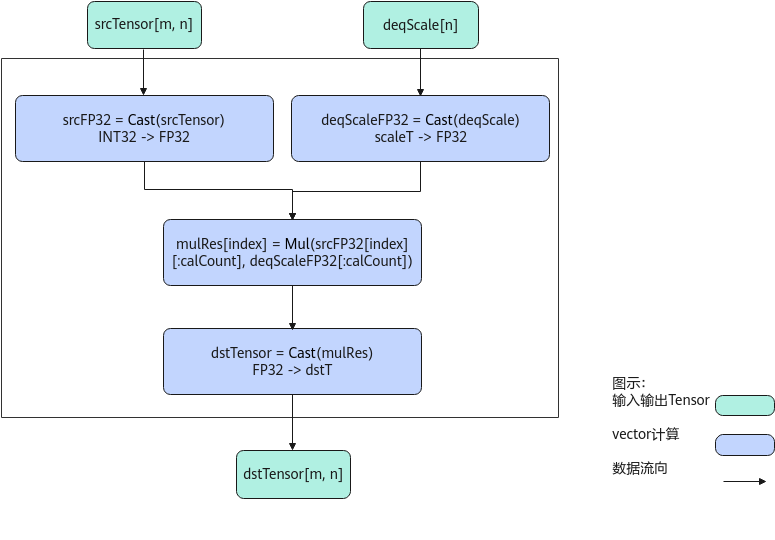
计算过程分为如下几步,均在Vector上进行:
- 精度转换:将srcTensor和deqScale都转换成FP32精度的tensor,分别得到srcFP32和deqScaleFP32;
- Mul计算:srcFP32一共有m行,每行长度为n;通过m次循环,将srcFP32的每行与deqscaleFP32相乘,通过mask控制仅对前dequantParams.calcount个数进行mul计算,图中index的取值范围为 [0, m),对应srcFP32的每一行;计算所得结果为mulRes,shape为[m, n];
- 结果数据精度转换:mulRes从FP32转换成dstT类型的tensor,所得结果为dstTensor,shape为[m, n]。
函数原型
- 反量化参数deqScale为矢量
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入临时空间
1 2
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT, DeQuantMode mode = DeQuantMode::DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW> __aicore__ inline void AscendDequant(const LocalTensor<dstT>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<int32_t>& srcTensor, const LocalTensor<scaleT>& deqScale, const LocalTensor<uint8_t>& sharedTmpBuffer, DequantParams params)
- 接口框架申请临时空间
1 2
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT, DeQuantMode mode = DeQuantMode::DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW> __aicore__ inline void AscendDequant(const LocalTensor<dstT>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<int32_t>& srcTensor, const LocalTensor<scaleT>& deqScale, DequantParams params)
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入临时空间
- 反量化参数deqScale为标量
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入临时空间
1 2
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT, DeQuantMode mode = DeQuantMode::DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW> __aicore__ inline void AscendDequant(const LocalTensor<dstT>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<int32_t>& srcTensor, const scaleT deqScale, const LocalTensor<uint8_t>& sharedTmpBuffer, DequantParams params)
- 接口框架申请临时空间
1 2
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT, DeQuantMode mode = DeQuantMode::DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW> __aicore__ inline void AscendDequant(const LocalTensor<dstT>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<int32_t>& srcTensor, const scaleT deqScale, DequantParams params)
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入临时空间
由于该接口的内部实现中涉及复杂的数学计算,需要额外的临时空间来存储计算过程中的中间变量。临时空间支持接口框架申请和开发者通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入两种方式。
- 接口框架申请临时空间,开发者无需申请,但是需要预留临时空间的大小。
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入,使用该tensor作为临时空间进行处理,接口框架不再申请。该方式开发者可以自行管理sharedTmpBuffer内存空间,并在接口调用完成后,复用该部分内存,内存不会反复申请释放,灵活性较高,内存利用率也较高。
接口框架申请的方式,开发者需要预留临时空间;通过sharedTmpBuffer传入的情况,开发者需要为sharedTmpBuffer申请空间。临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方式如下:通过GetAscendDequantMaxMinTmpSize中提供的GetAscendDequantMaxMinTmpSize接口获取需要预留空间的范围大小。
以下接口不推荐使用,新开发内容不要使用如下接口:
1 2 |
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT, DeQuantMode mode = DeQuantMode::DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW> __aicore__ inline void AscendDequant(const LocalTensor<dstT>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<int32_t>& srcTensor, const LocalTensor<scaleT>& deqScale, const LocalTensor<uint8_t>& sharedTmpBuffer, const uint32_t calCount) |
1 2 |
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT, DeQuantMode mode = DeQuantMode::DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW> __aicore__ inline void AscendDequant(const LocalTensor<dstT>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<int32_t>& srcTensor, const LocalTensor<scaleT>& deqScale, const LocalTensor<uint8_t>& sharedTmpBuffer) |
1 2 |
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT, DeQuantMode mode = DeQuantMode::DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW> __aicore__ inline void AscendDequant(const LocalTensor<dstT>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<int32_t>& srcTensor, const LocalTensor<scaleT>& deqScale, const uint32_t calCount) |
1 2 |
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT, DeQuantMode mode = DeQuantMode::DEQUANT_WITH_SINGLE_ROW> __aicore__ inline void AscendDequant(const LocalTensor<dstT>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<int32_t>& srcTensor, const LocalTensor<scaleT>& deqScale) |
参数说明
|
参数名 |
描述 |
|---|---|
|
dstT |
目的操作数的数据类型。 |
|
scaleT |
deqScale的数据类型。 |
|
mode |
决定当DequantParams为{1, n, calCount}时的计算逻辑,传入enum DeQuantMode,支持以下 2 种配置:
|
|
参数名 |
输入/输出 |
描述 |
|---|---|---|
|
dstTensor |
输出 |
目的操作数。类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float/bfloat16_t Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float
|
|
srcTensor |
输入 |
源操作数。类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:int32_t Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:int32_t shape为 [m, n],n个输入数据所占字节数要求32字节对齐。 |
|
deqScale |
输入 |
源操作数。类型为标量或者LocalTensor。类型为LocalTensor时,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,当deqScale为矢量时,支持的数据类型为:uint64_t/float/bfloat16_t;当deqScale为标量时,支持的数据类型为bfloat16_t/float。 Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,当deqScale为矢量时,支持的数据类型为:uint64_t/float;当deqScale为标量时,支持的数据类型为float。 |
|
sharedTmpBuffer |
输入 |
临时缓存。类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方式请参考GetAscendDequantMaxMinTmpSize。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:uint8_t Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:uint8_t |
|
params |
输入 |
srcTensor的shape信息。DequantParams类型,具体定义如下: struct DequantParams
{
uint32_t m; // srcTensor的行数
uint32_t n; // srcTensor的列数
uint32_t calCount; // 针对srcTensor每一行,前calCount个数为有效数据,与deqScale的前calCount个数或者deqScale标量进行乘法计算
};
|
返回值
无
支持的型号
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
约束说明
- 不支持源操作数与目的操作数地址重叠。
- 操作数地址偏移对齐要求请参见通用约束。
调用示例
#include "kernel_operator.h"
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT>
class KernelAscendDequant
{
public:
__aicore__ inline KernelAscendDequant() {}
__aicore__ inline void Init(GM_ADDR srcGm, GM_ADDR dstGm, GM_ADDR deqScaleGm,
uint32_t m, uint32_t n, uint32_t scaleSize)
{
m_ = m; // m = 4
n_ = n; // n = 8
dataSize_ = m * n; // dataSize_ = 32
scaleSize_ = scaleSize; // scaleSize = 8
src_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ int32_t *>(srcGm), dataSize_);
deq_scale_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ scaleT *>(deqScaleGm), scaleSize_);
dst_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ dstT *>(dstGm), dataSize_);
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueX, 1, dataSize_ * sizeof(int32_t));
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueDeqscale, 1, scaleSize_ * sizeof(scaleT));
pipe.InitBuffer(outQueue, 1, dataSize_ * sizeof(dstT));
}
__aicore__ inline void Process()
{
CopyIn();
Compute();
CopyOut();
}
private:
__aicore__ inline void CopyIn()
{
AscendC::LocalTensor<int32_t> srcLocal = inQueueX.AllocTensor<int32_t>();
AscendC::DataCopy(srcLocal, src_global, dataSize_);
inQueueX.EnQue(srcLocal);
AscendC::LocalTensor<scaleT> deqscaleLocal = inQueueDeqscale.AllocTensor<scaleT>();
AscendC::DataCopy(deqscaleLocal, deq_scale_global, scaleSize_);
inQueueDeqscale.EnQue(deqscaleLocal);
}
__aicore__ inline void Compute()
{
AscendC::LocalTensor<dstT> dstLocal = outQueue.AllocTensor<dstT>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<int32_t> srcLocal = inQueueX.DeQue<int32_t>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<scaleT> deqscaleLocal = inQueueDeqscale.DeQue<scaleT>();
AscendC::AscendDequant(dstLocal, srcLocal, deqscaleLocal, {m_, n_, deqscaleLocal.GetSize()});
outQueue.EnQue<dstT>(dstLocal);
inQueueX.FreeTensor(srcLocal);
inQueueDeqscale.FreeTensor(deqscaleLocal);
}
__aicore__ inline void CopyOut()
{
AscendC::LocalTensor<dstT> dstLocal = outQueue.DeQue<dstT>();
AscendC::DataCopy(dst_global, dstLocal, dataSize_);
outQueue.FreeTensor(dstLocal);
}
private:
AscendC::GlobalTensor<int32_t> src_global;
AscendC::GlobalTensor<scaleT> deq_scale_global;
AscendC::GlobalTensor<dstT> dst_global;
AscendC::TPipe pipe;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueX;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueDeqscale;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> outQueue;
uint32_t dataSize_ = 0;
uint32_t scaleSize_ = 0;
uint32_t m_ = 0;
uint32_t n_ = 0;
};
template <typename dstT, typename scaleT>
__aicore__ void kernel_ascend_dequant_operator(GM_ADDR srcGm, GM_ADDR dstGm, GM_ADDR deqScaleGm, uint32_t m, uint32_t n, uint32_t scaleSize)
{
KernelAscendDequant<dstT, scaleT> op;
op.Init(srcGm, dstGm, deqScaleGm, m, n, scaleSize);
op.Process();
}
结果示例如下:
输入数据(srcLocal) int32_t数据类型: [ -8 5 -5 -7 -3 -8 3 6 9 2 -5 0 0 -5 -7 0 -6 0 -2 3 -2 8 5 2 2 2 -4 5 -4 4 -8 3 ] 反量化参数deqScale float数据类型: [ 10.433567 10.765296 -30.694275 -65.47741 8.386527 -89.646194 65.11153 42.213394] 输出数据(dstLocal) float数据类型: [-83.46854 53.82648 153.47137 458.34186 -25.15958 717.16956 195.33458 253.28036 93.9021 21.530592 153.47137 -0. 0. 448.23096 -455.7807 0. -62.601402 0. 61.38855 -196.43222 -16.773054 -717.16956 325.55762 84.42679 20.867134 21.530592 122.7771 -327.38705 -33.54611 -358.58478 -520.8922 126.64018 ]