随路格式转换
功能说明
随路格式转换数据搬运,适用于在搬运时进行格式转换。
函数原型
- 源操作数为GlobalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor
1 2 3
// 支持ND2NZ格式转换 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const GlobalTensor<T>& srcGlobal, const Nd2NzParams& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表1 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为GlobalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数和目的操作数的数据类型 (两者保持一致)
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
GM -> VECIN
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
GM -> A1 / B1
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
GM -> VECIN
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / bfloat16_t / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
GM -> A1 / B1
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / bfloat16_t / float
注意:使用该接口时需要预留8K的Unified Buffer空间,作为接口的临时数据存放区
- 源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为GlobalTensor
- 支持NZ2ND格式转换
1 2 3
// 支持NZ2ND格式转换 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const GlobalTensor<T>& dstGlobal, const LocalTensor<T>& srcLocal, const Nz2NdParamsFull& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表2 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为GlobalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数和目的操作数的数据类型 (两者保持一致)
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
VECOUT -> GM
int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
CO2 -> GM
int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
VECOUT -> GM
int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / bfloat16_t / float
- 可以通过参数控制使能NZ2ND功能,同时包含量化、relu等功能
1 2 3
// 可以通过参数控制使能NZ2ND功能,同时包含量化、relu等功能 template <typename T, typename U> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const GlobalTensor<T>& dstGlobal, const LocalTensor<U>& srcLocal, const DataCopyCO12DstParams& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表3 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为GlobalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数的数据类型
目的操作数的数据类型
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
CO1 -> GM
float
uint8_t/int8_t/half/bfloat16_t/float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
CO1 -> GM
int32_t
uint8_t/int8_t/half/int16_t/int32_t
- 支持NZ2ND格式转换
- 源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor
- 支持ND2NZ格式转换
1 2 3
// 支持ND2NZ格式转换 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const LocalTensor<T>& srcGlobal, const Nd2NzParams& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表4 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数和目的操作数的数据类型 (两者保持一致)
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
VECIN / VECCALC / VECOUT -> TSCM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / bfloat16_t / float
- 包含量化、relu等功能
1 2
template <typename T, typename U> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const LocalTensor<U>& srcLocal, const DataCopyCO12DstParams& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表5 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数的数据类型
目的操作数的数据类型
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
CO1 -> A1
float
uint8_t/int8_t/half/bfloat16_t
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
CO1 -> A1
int32_t
uint8_t/int8_t/half/int16_t
- 支持ND2NZ格式转换
参数说明
参数名称 |
输入/输出 |
含义 |
|---|---|---|
dstLocal, dstGlobal |
输出 |
目的操作数,类型为LocalTensor或GlobalTensor。支持的数据类型为:half/int16_t/uint16_t/float/int32_t/uint32_t/int8_t/uint8_t。 |
srcLocal, srcGlobal |
输入 |
源操作数,类型为LocalTensor或GlobalTensor。支持的数据类型为:half/int16_t/uint16_t/float/int32_t/uint32_t/int8_t/uint8_t。 |
intriParams |
输入 |
搬运参数,类型为Nd2NzParams/Nz2NdParamsFull/DataCopyCO12DstParams。 |
- Nd2NzParams参数解析
表7 Nd2NzParams结构体参数定义 参数名称
含义
ndNum
传输nd矩阵的数目,取值范围:ndNum∈[0, 4095]。
nValue
nd矩阵的行数,取值范围:nValue∈[0, 16384]。
dValue
nd矩阵的列数,取值范围:dValue∈[0, 65535]。
srcNdMatrixStride
源操作数相邻nd矩阵起始地址间的偏移,取值范围:srcNdMatrixStride∈[0, 65535],单位:element。
srcDValue
源操作数同一nd矩阵的相邻行起始地址间的偏移,取值范围:srcDValue∈[1, 65535],单位:element。
dstNzC0Stride
ND转换到NZ格式后,源操作数中的一行会转换为目的操作数的多行。dstNzC0Stride表示,目的nz矩阵中,来自源操作数同一行的多行数据相邻行起始地址间的偏移,取值范围:dstNzC0Stride∈[1, 16384],单位:C0_SIZE(32B)。
dstNzNStride
目的nz矩阵中,Z型矩阵相邻行起始地址之间的偏移。取值范围:dstNzNStride∈[1, 16384],单位:C0_SIZE(32B)。
dstNzMatrixStride
目的nz矩阵中,相邻nz矩阵起始地址间的偏移,取值范围:dstNzMatrixStride∈[1, 65535],单位:element。
ND2NZ转换示意图如下,样例中参数设置值和解释说明如下:
- ndNum = 2,表示传输nd矩阵的数目为2 (nd矩阵1为A1~A2 + B1~B2, nd矩阵2为C1~C2 + D1~D2)。
- nValue = 2,nd矩阵的行数,也就是矩阵的高度为2。
- dValue = 24,nd矩阵的列数,也就是矩阵的宽度为24个元素。
- srcNdMatrixStride = 144,表达相邻nd矩阵起始地址间的偏移,即为A1~C1的距离,即为9个datablock,9 * 16 = 144个元素。
- srcDValue = 48, 表示一行的所含元素个数,即为A1到B1的距离,即为3个datablock, 3 * 16 = 48个元素
- dstNzC0Stride = 11。ND转换到NZ格式后,源操作数中的一行会转换为目的操作数的多行,例如src中A1和A2为1行,dst中A1和A2被分为2行。多行数据起始地址之间的偏移就是A1和A2在dst中的偏移,偏移为11个datablock。
- dstNzNStride = 2,表达dst中一个ndMatrix, src的第x行和第x+1行之间的偏移,即A1和B1之间的距离,即为2个datablock。
- dstNzMatrixStride = 96,表达dst中第x个ndMatrix的起点和第x+1个ndMatrix的起点的偏移,即A1和C1之间的距离,即为6个datablock, 6 * 16 = 96个元素。
图1 ND2NZ转换示意图(half数据类型)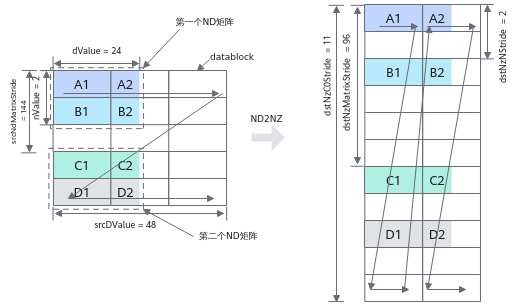
- Nz2NdParamsFull参数解析
表8 Nz2NdParamsFull结构体内参数定义 参数名称
含义
ndNum
传输nz矩阵的数目,取值范围:ndNum∈[0, 4095]。
nValue
nz矩阵的行数,取值范围:nValue∈[1, 8192]。
dValue
nz矩阵的列数,取值范围:dValue∈[1, 8192]。dValue必须为16的倍数。
srcNdMatrixStride
源相邻nz矩阵的偏移(头与头),取值范围:srcNdMatrixStride∈[1, 512],单位256 (16 * 16) 个元素。
srcNStride
源同一nz矩阵的相邻z排布的偏移(头与头),取值范围:srcNStride∈[0, 4096],单位16个元素。
dstDStride
目的nd矩阵的相邻行的偏移(头与头),取值范围:dstDStride∈[1, 65535],单位:element。
dstNdMatrixStride
目的nd矩阵中,来自源相邻nz矩阵的偏移(头与头),取值范围:dstNdMatrixStride∈[1, 65535],单位:element。
以half数据类型为例,NZ2ND转换示意图如下,样例中参数设置值和解释说明如下:
- ndNum = 2,表示源nz矩阵的数目为2 (nz矩阵1为A1~A4 + B1~B4, nz矩阵2为C1~C4 + D1~D4)。
- nValue = 4,nz矩阵的行数,也就是矩阵的高度为4。
- dValue = 32,nz矩阵的列数,也就是矩阵的宽度为32个元素。
- srcNdMatrixStride = 1,表达相邻NZ矩阵起始地址间的偏移,即为A1~C1的距离,即为256个元素(16个datablock * 16个元素per block)。
- srcNStride = 4, 表示同一个源NZ矩阵的相邻Z排布的偏移,即为A1到B1的距离,即为64个元素(4个datablock* 16元素per block)。
- dstDStride = 160,表达一个目的ND矩阵的相邻行之间的偏移,即A1和A2之间的距离,即为10个datablock,即10 * 16 = 160个元素。
- dstNdMatrixStride = 48,表达dst中第x个目的ND矩阵的起点和第x+1个目的ND矩阵的起点的偏移,即A1和C1之间的距离,即为3个datablock, 3 * 16 = 48个元素。
图2 NZ2ND转换示意图(half数据类型)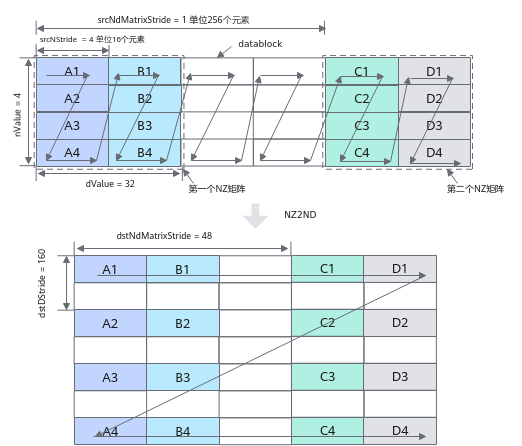
以float数据类型为例,NZ2ND转换示意图如下,样例中参数设置值和解释说明如下:
- ndNum = 2,表示源nz矩阵的数目为2 (nz矩阵1为A1~A8 + B1~B8, nz矩阵2为C1~C8 + D1~D8)。
- nValue = 4,nz矩阵的行数,也就是矩阵的高度为4。
- dValue = 32,nz矩阵的列数,也就是矩阵的宽度为32个元素。
- srcNdMatrixStride = 1,表达相邻NZ矩阵起始地址间的偏移,即为A1到C1的距离,即为256个元素(32个datablock * 8元素per block)
- srcNStride = 4, 表示同一个源NZ矩阵的相邻Z排布的偏移,即为A1到B1的距离,即为64个元素 (8个datablock * 8元素per block)。
- dstDStride = 144,表达一个目的ND矩阵的相邻行之间的偏移,即A1和A3之间的距离,即为18个datablock,即18 * 8 = 144个元素。
- dstNdMatrixStride = 40,表达dst中第x个目的ND矩阵的起点和第x+1个目的ND矩阵的起点的偏移,即A1和C1之间的距离,即为5个datablock, 5 * 8 = 40个元素。
图3 NZ2ND转换示意图(float数据类型)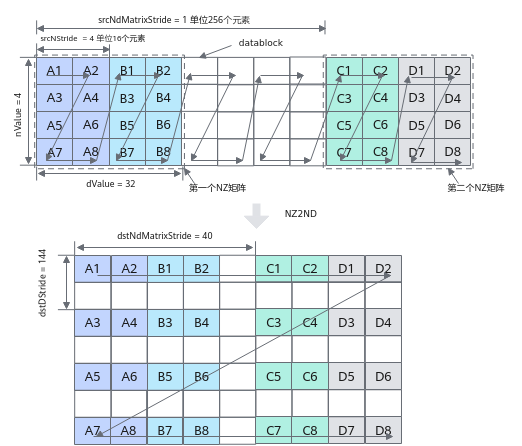
- DataCopyCO12DstParams参数解析
下文中的C0取值:一般情况下,C0 = 16;使能channelSplit(channel切分)时,C0 = 8。
表9 DataCopyCO12DstParams结构体参数定义 参数名称
含义
nSize
srcLocal横向方向的size大小。
- 不使能NZ2ND功能,必须为C0的倍数,此时连续传输数据块的个数为nSize/C0。
- 使能NZ2ND功能,不受限制。
mSize
srcLocal纵向方向的size大小。
- 不使能NZ2ND功能,连续传输数据块的大小为mSize * C0个元素的长度。
- 使能NZ2ND功能,NZ/ND矩阵的大小为mSize*nSize。
dstStride
srcStride
quantPre
用于控制量化模式,QuantMode_t类型,具体定义如下。默认值为QuantMode_t::NoQuant,即不使能量化功能。
配置为scalar量化时,需要调用SetFixpipePreQuantFlag接口来设置scalar量化参数;配置为tensor量化时,需要调用SetFixPipeConfig来设置tensor量化参数。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
enum QuantMode_t { NoQuant, // 不使能量化功能 F322F16, // float量化成half, scalar量化 F322BF16, // float量化成bfloat16_t, scalar量化 DEQF16, // int32_t量化成half, scalar量化 VDEQF16, // int32_t量化成half,tensor量化 QF322B8_PRE, // float量化成int8_t/uint8_t,scalar量化 VQF322B8_PRE, // float量化成int8_t/uint8_t,tensor量化 REQ8, // int32_t量化成int8_t/uint8_t,scalar量化 VREQ8, // int32_t量化成int8_t/uint8_t,tensor量化 };
reluPre
用于配置relu操作的模式,类型为uint8_t,取值如下:
- 0:不使能relu
- 1:Normal relu
channelSplit
类型为bool,配置是否使能channel切分,对于float类型的dstLocal生效。
- false:不使能
- true:使能
nz2ndEn
类型为bool,配置是否使能NZ2ND的格式转换,仅在L0C->GM通路生效。
如果要使能NZ2ND的功能需要同步调用SetFixpipeNz2ndFlag来设置格式转换的相关配置信息。
- false:不使能
- true:使能
支持的型号
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
调用示例
- 随路格式转换数据搬运,nz2nd
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55
#include "kernel_operator.h" class KernelDataCopyUb2GmNz2Nd { public: __aicore__ inline KernelDataCopyUb2GmNz2Nd() {} __aicore__ inline void Init(__gm__ uint8_t* dstGm, __gm__ uint8_t* srcGm) { AscendC::Nz2NdParamsFull intriParamsIn{1, 32, 32, 1, 32, 32, 1}; intriParams = intriParamsIn; srcGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ half *)srcGm); dstGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ half *)dstGm); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueSrcVecIn, 1, intriParams.nValue * intriParams.dValue * sizeof(half)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueSrcVecOut, 1, intriParams.nValue * intriParams.dValue * sizeof(half)); } __aicore__ inline void Process() { CopyIn(); Compute(); CopyOut(); } private: __aicore__ inline void CopyIn() { AscendC::LocalTensor<half> srcLocal = inQueueSrcVecIn.AllocTensor<half>(); AscendC::DataCopy(srcLocal, srcGlobal, intriParams.nValue * intriParams.dValue); inQueueSrcVecIn.EnQue(srcLocal); } __aicore__ inline void Compute() { AscendC::LocalTensor<half> dstLocal = inQueueSrcVecIn.DeQue<half>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<half> srcOutLocal = inQueueSrcVecOut.AllocTensor<half>(); AscendC::DataCopy(srcOutLocal, dstLocal, intriParams.nValue * intriParams.dValue); inQueueSrcVecOut.EnQue(srcOutLocal); inQueueSrcVecIn.FreeTensor(dstLocal); } __aicore__ inline void CopyOut() { AscendC::LocalTensor<half> srcOutLocalDe = inQueueSrcVecOut.DeQue<half>(); AscendC::DataCopy(dstGlobal, srcOutLocalDe, intriParams); inQueueSrcVecOut.FreeTensor(srcOutLocalDe); } private: AscendC::TPipe pipe; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueSrcVecIn; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> inQueueSrcVecOut; AscendC::GlobalTensor<half> srcGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<half> dstGlobal; AscendC::Nz2NdParamsFull intriParams; }; extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void kernel_data_copy_nz2nd_ub2out(__gm__ uint8_t* src_gm, __gm__ uint8_t* dst_gm) { KernelDataCopyUb2GmNz2Nd op; op.Init(dst_gm, src_gm); op.Process(); }
结果示例:
输入数据(srcGlobal): [1 2 3 ... 1024] 输出数据(dstGlobal):[1 2 ... 15 16 513 514 ... 527 528 17 18 ... 31 32 529 530 ... 543 544 ...497 498 ... 511 512 1009 1010... 1023 1024]
- 随路格式转换数据搬运,通路:CO1->A1、CO1->GM示例:mmad含有矩阵乘偏置,左矩阵和右矩阵的数据类型为int8_t,结果矩阵的数据类型为int32_t。量化模式DEQF16, scalar量化参数为0.5,将mmad计算出的结果由int32_t量化成half并搬出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220
#ifdef ASCENDC_CPU_DEBUG #include "tikicpulib.h" #endif #include "kernel_operator.h" #include "../../instrs/common_utils/register_utils.h" SET_G_CORE_TYPE_IS_AIC template <typename dst_T, typename fmap_T, typename weight_T, typename dstCO1_T> class KernelCubeDataCopy{ public: __aicore__ inline KernelCubeDataCopy(uint16_t CoutIn, uint8_t dilationHIn, uint8_t dilationWIn, QuantMode_t deqModeIn) { // ceiling of 16 Cout = CoutIn; dilationH = dilationHIn; dilationW = dilationWIn; C0 = 32 / sizeof(fmap_T); C1 = channelSize / C0; coutBlocks = (Cout + 16 - 1) / 16; ho = H - dilationH * (Kh - 1); wo = W - dilationW * (Kw - 1); howo = ho * wo; howoRound = ((howo + 16 - 1) / 16) * 16; featureMapA1Size = C1 * H * W * C0; // shape: [C1, H, W, C0] weightA1Size = C1 * Kh * Kw * Cout * C0; // shape: [C1, Kh, Kw, Cout, C0] featureMapA2Size = howoRound * (C1 * Kh * Kw * C0); weightB2Size = (C1 * Kh * Kw * C0) * coutBlocks * 16; m = howo; k = C1 * Kh * Kw * C0; n = Cout; biasSize = Cout; // shape: [Cout] dstSize = coutBlocks * howo * 16; // shape: [coutBlocks, howo, 16] dstCO1Size = coutBlocks * howoRound * 16; fmRepeat = featureMapA2Size / (16 * C0); weRepeat = weightB2Size / (16 * C0); deqMode = deqModeIn; } __aicore__ inline void Init(__gm__ uint8_t* fmGm, __gm__ uint8_t* weGm, __gm__ uint8_t* biasGm, __gm__ uint8_t* deqGm, __gm__ uint8_t* dstGm) { fmGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ fmap_T*)fmGm); weGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ weight_T*)weGm); biasGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dstCO1_T*)biasGm); deqGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ uint64_t*)deqGm); dstGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dst_T*)dstGm); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueFmA1, 1, featureMapA1Size * sizeof(fmap_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueFmA2, 1, featureMapA2Size * sizeof(fmap_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueWeB1, 1, weightA1Size * sizeof(weight_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueWeB2, 1, weightB2Size * sizeof(weight_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueBiasA1, 1, biasSize * sizeof(dstCO1_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueDeqA1, 1, dstCO1Size * sizeof(uint64_t)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueDeqFB, 1, dstCO1Size * sizeof(uint64_t)); pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueCO1, 1, dstCO1Size * sizeof(dstCO1_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueA1, 1, dstCO1Size * sizeof(dst_T)); } __aicore__ inline void Process() { CopyIn(); Split(); Compute(); CopyOut(); } private: __aicore__ inline void CopyIn() { AscendC::LocalTensor<fmap_T> featureMapA1 = inQueueFmA1.AllocTensor<fmap_T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<weight_T> weightB1 = inQueueWeB1.AllocTensor<weight_T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dstCO1_T> biasA1 = inQueueBiasA1.AllocTensor<dstCO1_T>(); AscendC::DataCopy(featureMapA1, fmGlobal, { 1, static_cast<uint16_t>(featureMapA1Size * sizeof(fmap_T) / 32), 0, 0 }); AscendC::DataCopy(weightB1, weGlobal, { 1, static_cast<uint16_t>(weightA1Size * sizeof(weight_T) / 32), 0, 0 }); AscendC::DataCopy(biasA1, biasGlobal, { 1, static_cast<uint16_t>(biasSize * sizeof(dstCO1_T) / 32), 0, 0 }); inQueueFmA1.EnQue(featureMapA1); inQueueWeB1.EnQue(weightB1); inQueueBiasA1.EnQue(biasA1); } __aicore__ inline void Split() { AscendC::LocalTensor<fmap_T> featureMapA1 = inQueueFmA1.DeQue<fmap_T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<weight_T> weightB1 = inQueueWeB1.DeQue<weight_T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<fmap_T> featureMapA2 = inQueueFmA2.AllocTensor<fmap_T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<weight_T> weightB2 = inQueueWeB2.AllocTensor<weight_T>(); uint8_t padList[] = {0, 0, 0, 0}; // load3dv2 AscendC::LoadData(featureMapA2, featureMapA1, { padList, H, W, channelSize, k, howoRound, 0, 0, 1, 1, Kw, Kh, dilationW, dilationH, false, false, 0 }); // load2d AscendC::LoadData(weightB2, weightB1, { 0, weRepeat, 1, 0, 0, false, 0 }); inQueueFmA2.EnQue<fmap_T>(featureMapA2); inQueueWeB2.EnQue<weight_T>(weightB2); inQueueFmA1.FreeTensor(featureMapA1); inQueueWeB1.FreeTensor(weightB1); } __aicore__ inline void Compute() { AscendC::LocalTensor<fmap_T> featureMapA2 = inQueueFmA2.DeQue<fmap_T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<weight_T> weightB2 = inQueueWeB2.DeQue<weight_T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dstCO1_T> dstCO1 = outQueueCO1.AllocTensor<dstCO1_T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dstCO1_T> biasA1 = inQueueBiasA1.DeQue<dstCO1_T>(); // C = A * B + bias // m: 左矩阵Height, k: 左矩阵Width, n: 右矩阵Width AscendC::Mmad(dstCO1, featureMapA2, weightB2, biasA1, { m, n, k, true, 0, false, false, false }); outQueueCO1.EnQue<dstCO1_T>(dstCO1); inQueueFmA2.FreeTensor(featureMapA2); inQueueWeB2.FreeTensor(weightB2); } __aicore__ inline void CopyOut() { AscendC::LocalTensor<dstCO1_T> dstCO1 = outQueueCO1.DeQue<dstCO1_T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dst_T> dstA1 = outQueueA1.DeQue<dst_T>(); // 使能DEQF16量化,量化参数设置为0.5 float tmp = (float)0.5; // 将float的tmp转换成uint64_t的deqScalar uint64_t deqScalar = static_cast<uint64_t>(*reinterpret_cast<int32_t*>(&tmp)); bool nz2ndEn = false; // nz2nd不使能时,nSize必须为16的倍数 uint16_t nSize = coutBlocks * 16; uint16_t mSize = m; // srcStride必须为16的倍数 uint16_t srcStride = (m + 16 - 1) / 16 * 16; // nz2nd不使能时,dstStride为burst头到头的距离,且为32B对齐 uint32_t dstStride = m * sizeof(dst_T) * 16 / 32; if (nz2ndEn) { // nd矩阵的数量为1,src_nd_stride与dst_nd_stride填0 AscendC::SetFixpipeNz2ndFlag(1, 0, 0); // nz2nd使能时,nSize可以不为16的倍数,与Mmad的n保持一致 nSize = n; // nz2nd使能时,dstStride表示同一nd矩阵的相邻连续行的间隔,与n保持一致 dstStride = nSize; }; // 不使能relu与channelSplit AscendC::DataCopyCO12DstParams intriParams(nSize, mSize, dstStride, srcStride, deqMode, 0, false, nz2ndEn); // mov l0c to gm, deq scalar quant AscendC::SetFixpipePreQuantFlag(deqScalar); // 设置量化参数 AscendC::PipeBarrier<PIPE_FIX>(); AscendC::DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstCO1, intriParams); // // mov l0c to gm, deq tensor quant // // 需要额外申请deq tensor的gm空间,将值搬运到workA1 // AscendC::LocalTensor<uint64_t> workA1 = inQueueDeqA1.DeQue<uint64_t>(); // // deq tensor的size // uint16_t deqSize = 128; // AscendC::DataCopy(workA1, deqGlobal, deqSize); // // deq tensor在fix上的地址 // AscendC::LocalTensor<uint64_t> deqFB = inQueueDeqFB.AllocTensor<uint64_t>(); // // l1->fix, burst_len unit is 128Bytes // uint16_t fbufBurstLen = deqSize / 128; // AscendC::DataCopyParams dataCopyParams(1, fbufBurstLen, 0, 0); // AscendC::DataCopy(deqFB, workA1, dataCopyParams); // // 设置量化tensor // AscendC::SetFixPipeConfig(deqFB); // AscendC::PipeBarrier<PIPE_FIX>(); // AscendC::DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstCO1, intriParams); // inQueueDeqA1.FreeTensor(workA1); // inQueueDeqFB.FreeTensor(deqFB); // // mov l0c to l1, deq scalar quant, and then mov l1 to gm // AscendC::SetFixpipePreQuantFlag(deqScalar); // 设置量化参数 // AscendC::PipeBarrier<PIPE_FIX>(); // AscendC::DataCopy(dstA1, dstCO1, intriParams); // AscendC::DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstA1, dstCO1Size); // // mov l0c to l1, deq tensor quant, and then mov l1 to gm // AscendC::LocalTensor<uint64_t> workA1 = inQueueDeqA1.DeQue<uint64_t>(); // uint16_t deqSize = 128; // AscendC::DataCopy(workA1, deqGlobal, deqSize); // AscendC::LocalTensor<uint64_t> deqFB = inQueueDeqFB.AllocTensor<uint64_t>(); // uint16_t fbufBurstLen = deqSize / 128; // AscendC::DataCopyParams dataCopyParams(1, fbufBurstLen, 0, 0); // AscendC::DataCopy(deqFB, workA1, dataCopyParams); // // 设置量化tensor // AscendC::SetFixPipeConfig(deqFB); // AscendC::PipeBarrier<PIPE_FIX>(); // AscendC::DataCopy(dstA1, dstCO1, intriParams); // AscendC::DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstA1, dstCO1Size); // inQueueDeqA1.FreeTensor(workA1); // inQueueDeqFB.FreeTensor(deqFB); // outQueueCO1.FreeTensor(dstCO1); // outQueueA1.FreeTensor(dstA1); } private: AscendC::TPipe pipe; // feature map queue AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::A1, 1> inQueueFmA1; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::A2, 1> inQueueFmA2; // weight queue AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::B1, 1> inQueueWeB1; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::B2, 1> inQueueWeB2; // bias queue AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::A1, 1> inQueueBiasA1; // deq tensor queue AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::A1, 1> inQueueDeqA1; // fb dst of deq tensor AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::C2PIPE2GM, 1> inQueueDeqFB; // dst queue AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::CO1, 1> outQueueCO1; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::A1, 1> outQueueA1; AscendC::GlobalTensor<fmap_T> fmGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<weight_T> weGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<dst_T> dstGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<uint64_t> deqGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<dstCO1_T> biasGlobal; uint16_t channelSize = 32; uint16_t H = 4, W = 4; uint8_t Kh = 2, Kw = 2; uint16_t Cout; uint16_t C0, C1; uint8_t dilationH, dilationW; uint16_t coutBlocks, ho, wo, howo, howoRound; uint32_t featureMapA1Size, weightA1Size, featureMapA2Size, weightB2Size, biasSize, dstSize, dstCO1Size; uint16_t m, k, n; uint8_t fmRepeat, weRepeat; QuantMode_t deqMode = QuantMode_t::NoQuant; }; #define KERNEL_CUBE_DATACOPY(dst_type, fmap_type, weight_type, dstCO1_type, CoutIn, dilationHIn, dilationWIn, deqModeIn) \ extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void cube_datacopy_kernel_##fmap_type(__gm__ uint8_t* fmGm, __gm__ uint8_t* weGm, \ __gm__ uint8_t* biasGm, __gm__ uint8_t* deqGm, __gm__ uint8_t* dstGm) \ { \ if (g_coreType == AscendC::AIV) { \ return; \ } \ KernelCubeDataCopy<dst_type, fmap_type, weight_type, dstCO1_type> op(CoutIn, dilationHIn, dilationWIn, \ deqModeIn); \ op.Init(fmGm, weGm, biasGm, deqGm, dstGm); \ op.Process(); \ } KERNEL_CUBE_DATACOPY(half, int8_t, int8_t, int32_t, 128, 1, 1, QuantMode_t::DEQF16);