普通数据搬运
函数功能
普通数据搬运接口,适用于连续和不连续数据搬运。
函数原型
- 源操作数为GlobalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor
// 支持连续和不连续 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const GlobalTensor<T>& srcGlobal, const DataCopyParams& intriParams); // 支持连续 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const GlobalTensor<T>& srcGlobal, const uint32_t calCount);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表1 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为GlobalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数和目的操作数的数据类型 (两者保持一致)
Atlas 训练系列产品
GM -> VECIN
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas 训练系列产品
GM -> A1 / B1
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
GM -> VECIN
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
GM -> A1 / B1
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品Vector Core
GM -> VECIN
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
GM -> VECIN
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
GM -> A1 / B1 / C1
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float / uint64_t
Atlas 200I/500 A2推理产品
GM -> VECIN
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
- 源操作数和目的操作数都为LocalTensor
// 支持连续和不连续 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const LocalTensor <T>& srcLocal, const DataCopyParams& intriParams); // 支持连续 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const LocalTensor <T>& srcLocal, const uint32_t calCount);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表2 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数和目的操作数都为LocalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数和目的操作数的数据类型 (两者保持一致)
Atlas 训练系列产品
VECIN -> VECCALC, VECCALC->VECOUT
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
VECIN -> VECCALC, VECCALC->VECOUT
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT -> A1/B1
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
VECIN -> VECCALC, VECCALC->VECOUT
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT -> TSCM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
C1 -> C2
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
A1/B1/C1->C2PIPE2GM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / uint64_t / half / float
- 源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为GlobalTensor
// 支持连续和不连续 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const GlobalTensor <T>& dstGlobal, const LocalTensor <T>& srcLocal, const DataCopyParams& intriParams); // 支持连续 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const GlobalTensor <T>& dstGlobal, const LocalTensor <T>& srcLocal, const uint32_t calCount);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表3 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为GlobalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数和目的操作数的数据类型 (两者保持一致)
Atlas 训练系列产品
VECOUT -> GM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
VECOUT -> GM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
CO2 -> GM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品Vector Core
VECOUT -> GM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
VECOUT -> GM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
A1/B1 -> GM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas 200I/500 A2推理产品
VECOUT -> GM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
- 源操作数和目的操作数都为LocalTensor,支持源操作数和目的操作数类型不一致
template <typename dst_T, typename src_T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<dst_T> &dstLocal, const LocalTensor<src_T> &srcLocal, const DataCopyParams& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表4 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数和目的操作数都为LocalTensor,支持源操作数和目的操作数类型不一致) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数数据类型
目的操作数数据类型
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
C1 -> C2
half
float
参数说明
参数名称 |
输入/输出 |
含义 |
|---|---|---|
dstLocal, dstGlobal |
输出 |
目的操作数,类型为LocalTensor或GlobalTensor。支持的数据类型为:half/int16_t/uint16_t/float/int32_t/uint32_t/int8_t/uint8_t。 当dstLocal位于C2时,起始地址要求64B对齐;dstLocal位于C2PIPE2GM时,起始地址要求128B对齐;其他情况均为32字节对齐。 |
srcLocal, srcGlobal |
输入 |
源操作数,类型为LocalTensor或GlobalTensor。支持的数据类型为:half/int16_t/uint16_t/float/int32_t/uint32_t/int8_t/uint8_t。 |
intriParams |
输入 |
搬运参数,DataCopyParams类型,DataCopyParams结构定义请参考表6。 |
calCount |
输入 |
参与搬运的元素个数。 |
参数名称 |
含义 |
|---|---|
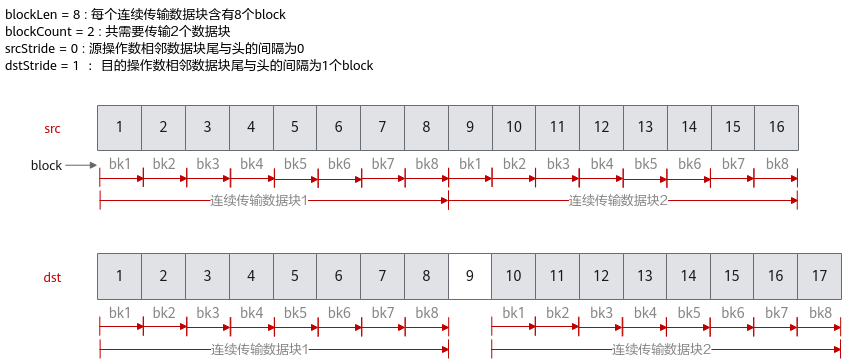
blockCount |
指定该指令包含的连续传输数据块个数,取值范围:blockCount∈[1, 4095]。 |
blockLen |
指定该指令每个连续传输数据块长度,单位为datablock(32Bytes)。取值范围:blockLen∈[1, 65535]。 特别的,当dstLocal位于C2PIPE2GM时,单位为128B;当dstLocal位于C2时,单位为64B。 |
srcStride |
源操作数,相邻连续数据块的间隔(前面一个数据块的尾与后面数据块的头的间隔),单位为datablock(32Bytes)。 |
dstStride |
目的操作数,相邻连续数据块间的间隔(前面一个数据块的尾与后面数据块的头的间隔),单位为datablock(32Bytes)。 特别的,当dstLocal位于C2PIPE2GM时,单位为128B;当dstLocal位于C2时,单位为64B。 |
下面的样例呈现了DataCopyParams结构体参数的使用方法,样例中完成了2个连续传输数据块的搬运,每个数据块含有8个block,源操作数相邻数据块之间无间隔,目的操作数相邻数据块尾与头之间间隔1个block。
支持的型号
Atlas 训练系列产品
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
Atlas推理系列产品Vector Core
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
Atlas 200I/500 A2推理产品
注意事项
- DataCopy的搬运量要求为32byte的倍数,因此使用普通数据搬运接口(连续数据搬运,包含calCount参数)时,calCount * sizeof(T)需要32byte对齐,若不对齐,搬运量将对32byte做向下取整。
- 硬件在执行数据搬运时会以block作为基本单位,而 1 block = 32 Byte,故使用者可以尝试通过每次指令处理32Byte整数倍大小的数据来提高指令的执行效率。
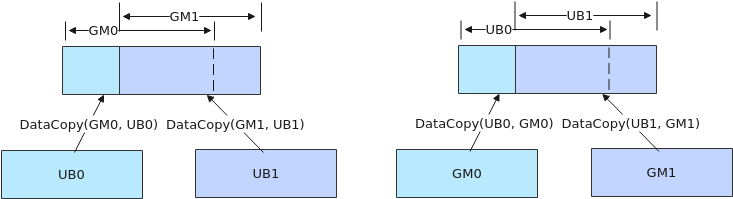
- 如果需要执行多个DataCopy指令,且DataCopy的目的地址存在重叠,需要通过调用PipeBarrier来插入同步指令,保证多个DataCopy指令的串行化,防止出现异常数据。如下图左侧示意图,执行两个DataCopy指令,搬运的目的GM地址存在重叠,两条搬运指令之间需要通过调用PipeBarrier<PIPE_MTE3>()添加MTE3搬出流水的同步;如下图右侧示意图所示,搬运的目的地址Unified Buffer存在重叠,两条搬运指令之间需要调用PipeBarrier<PIPE_MTE2>()添加MTE2搬入流水的同步。
调用示例
#include "kernel_operator.h"
namespace AscendC {
class KernelDataCopy {
public:
__aicore__ inline KernelDataCopy() {}
__aicore__ inline void Init(__gm__ uint8_t* src0Gm, __gm__ uint8_t* src1Gm, __gm__ uint8_t* dstGm)
{
src0Global.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ half*)src0Gm);
src1Global.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ half*)src1Gm);
dstGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ half*)dstGm);
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueSrc0, 1, 512 * sizeof(half));
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueSrc1, 1, 512 * sizeof(half));
pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueDst, 1, 512 * sizeof(half));
}
__aicore__ inline void Process()
{
CopyIn();
Compute();
CopyOut();
}
private:
__aicore__ inline void CopyIn()
{
LocalTensor<half> src0Local = inQueueSrc0.AllocTensor<half>();
LocalTensor<half> src1Local = inQueueSrc1.AllocTensor<half>();
DataCopy(src0Local, src0Global, 512);
DataCopy(src1Local, src1Global, 512);
inQueueSrc0.EnQue(src0Local);
inQueueSrc1.EnQue(src1Local);
}
__aicore__ inline void Compute()
{
LocalTensor<half> src0Local = inQueueSrc0.DeQue<half>();
LocalTensor<half> src1Local = inQueueSrc1.DeQue<half>();
LocalTensor<half> dstLocal = outQueueDst.AllocTensor<half>();
Add(dstLocal, src0Local, src1Local, 512);
outQueueDst.EnQue<half>(dstLocal);
inQueueSrc0.FreeTensor(src0Local);
inQueueSrc1.FreeTensor(src1Local);
}
__aicore__ inline void CopyOut()
{
LocalTensor<half> dstLocal = outQueueDst.DeQue<half>();
DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstLocal, 512);
outQueueDst.FreeTensor(dstLocal);
}
private:
TPipe pipe;
TQue<QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueSrc0, inQueueSrc1;
TQue<QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> outQueueDst;
GlobalTensor<half> src0Global, src1Global, dstGlobal;
};
} // namespace AscendC
extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void data_copy_kernel(__gm__ uint8_t* src0Gm, __gm__ uint8_t* src1Gm, __gm__ uint8_t* dstGm)
{
AscendC::KernelDataCopy op;
op.Init(src0Gm, src1Gm, dstGm);
op.Process();
}
输入数据(src0Global): [1 2 3 ... 512] 输入数据(src1Global): [1 2 3 ... 512] 输出数据(dstGlobal):[2 4 6 ... 1024]