随路格式转换
函数原型
- 源操作数为GlobalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor
// 支持ND2NZ格式转换 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const GlobalTensor<T>& srcGlobal, const Nd2NzParams& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表1 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为GlobalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数和目的操作数的数据类型 (两者保持一致)
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
GM -> VECIN
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
GM -> A1 / B1
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
GM -> VECIN
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
GM -> A1 / B1
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
注意:使用该接口时需要预留8K的Unified Buffer空间,作为接口的临时数据存放区
- 源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为GlobalTensor
- 支持NZ2ND格式转换
// 支持NZ2ND格式转换 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const GlobalTensor <T>& dstGlobal, const LocalTensor <T>& srcLocal, const Nz2NdParamsFull &intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表2 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为GlobalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数和目的操作数的数据类型 (两者保持一致)
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
VECOUT -> GM
int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
CO2 -> GM
int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
VECOUT -> GM
int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
- 可以通过参数控制使能NZ2ND功能,同时包含量化、relu等功能
// 可以通过参数控制使能NZ2ND功能,同时包含量化、relu等功能 template <typename T, typename U> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const GlobalTensor<T>& dstGlobal, const LocalTensor<U>& srcLocal, const DataCopyCO12DstParams& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表3 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为GlobalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数的数据类型
目的操作数的数据类型
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
CO1 -> GM
float
uint8_t/int8_t/half/bfloat16_t/float
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
CO1 -> GM
int32_t
uint8_t/int8_t/half/int16_t/int32_t
- 支持NZ2ND格式转换
- 源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor
- 支持ND2NZ格式转换
// 支持ND2NZ格式转换 template <typename T> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T> &dstLocal, const LocalTensor<T> &srcGlobal, const Nd2NzParams& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表4 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数和目的操作数的数据类型 (两者保持一致)
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
VECIN / VECCALC / VECOUT -> TSCM
int8_t / uint8_t / int16_t / uint16_t / int32_t / uint32_t / half / float
- 包含量化、relu等功能
template <typename T, typename U> __aicore__ inline void DataCopy(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const LocalTensor<U>& srcLocal, const DataCopyCO12DstParams& intriParams);
该原型接口支持的数据通路和数据类型如下所示:
表5 数据通路和数据类型(源操作数为LocalTensor,目的操作数为LocalTensor) 支持型号
数据通路
源操作数的数据类型
目的操作数的数据类型
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
CO1 -> A1
float
uint8_t/int8_t/half/bfloat16_t
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
CO1 -> A1
int32_t
uint8_t/int8_t/half/int16_t
- 支持ND2NZ格式转换
参数说明
参数名称 |
输入/输出 |
含义 |
|---|---|---|
dstLocal, dstGlobal |
输出 |
目的操作数,类型为LocalTensor或GlobalTensor。支持的数据类型为:half/int16_t/uint16_t/float/int32_t/uint32_t/int8_t/uint8_t。 |
srcLocal, srcGlobal |
输入 |
源操作数,类型为LocalTensor或GlobalTensor。支持的数据类型为:half/int16_t/uint16_t/float/int32_t/uint32_t/int8_t/uint8_t。 |
intriParams |
输入 |
搬运参数,类型为Nd2NzParams / Nz2NdParamsFull / DataCopyCO12DstParams。 |
- Nd2NzParams参数解析
表7 Nd2NzParams结构体参数定义 参数名称
含义
ndNum
传输nd矩阵的数目,取值范围:ndNum∈[0, 4095]。
nValue
nd矩阵的行数,取值范围:nValue∈[0, 16384]。
dValue
nd矩阵的列数,取值范围:dValue∈[0, 65535]。
srcNdMatrixStride
源操作数相邻nd矩阵起始地址间的偏移,取值范围:srcNdMatrixStride∈[0, 65535],单位:element。
srcDValue
源操作数同一nd矩阵的相邻行起始地址间的偏移,取值范围:srcDValue∈[1, 65535],单位:element。
dstNzC0Stride
ND转换到NZ格式后,源操作数中的一行会转换为目的操作数的多行。dstNzC0Stride表示,目的nz矩阵中,来自源操作数同一行的多行数据相邻行起始地址间的偏移,取值范围:dstNzC0Stride∈[1, 16384],单位:C0_SIZE(32B)。
dstNzNStride
目的nz矩阵中,Z型矩阵相邻行起始地址之间的偏移。取值范围:dstNzNStride∈[1, 16384],单位:C0_SIZE(32B)。
dstNzMatrixStride
目的nz矩阵中,相邻nz矩阵起始地址间的偏移,取值范围:dstNzMatrixStride∈[1, 65535],单位:element。
ND2NZ转换示意图如下,样例中参数设置值和解释说明如下:
- ndNum = 2,表示传输nd矩阵的数目为2 (nd矩阵1为A1~A2 + B1~B2, nd矩阵2为C1~C2 + D1~D2)。
- nValue = 2,nd矩阵的行数,也就是矩阵的高度为2。
- dValue = 24,nd矩阵的列数,也就是矩阵的宽度为24个元素。
- srcNdMatrixStride = 144,表达相邻nd矩阵起始地址间的偏移,即为A1~C1的距离,即为9个datablock,9 * 16 = 144个元素。
- srcDValue = 48, 表示一行的所含元素个数,即为A1到B1的距离,即为3个datablock, 3 * 16 = 48个元素
- dstNzC0Stride = 11。ND转换到NZ格式后,源操作数中的一行会转换为目的操作数的多行,例如src中A1和A2为1行,dst中A1和A2被分为2行。多行数据起始地址之间的偏移就是A1和A2在dst中的偏移,偏移为11个datablock。
- dstNzNStride = 2,表达dst中一个ndMatrix, src的第x行和第x+1行之间的偏移,即A1和B1之间的距离,即为2个datablock。
- dstNzMatrixStride = 96,表达dst中第x个ndMatrix的起点和第x+1个ndMatrix的起点的偏移,即A1和C1之间的距离,即为6个datablock, 6 * 16 = 96个元素。
图1 Nd2Nz转换示意图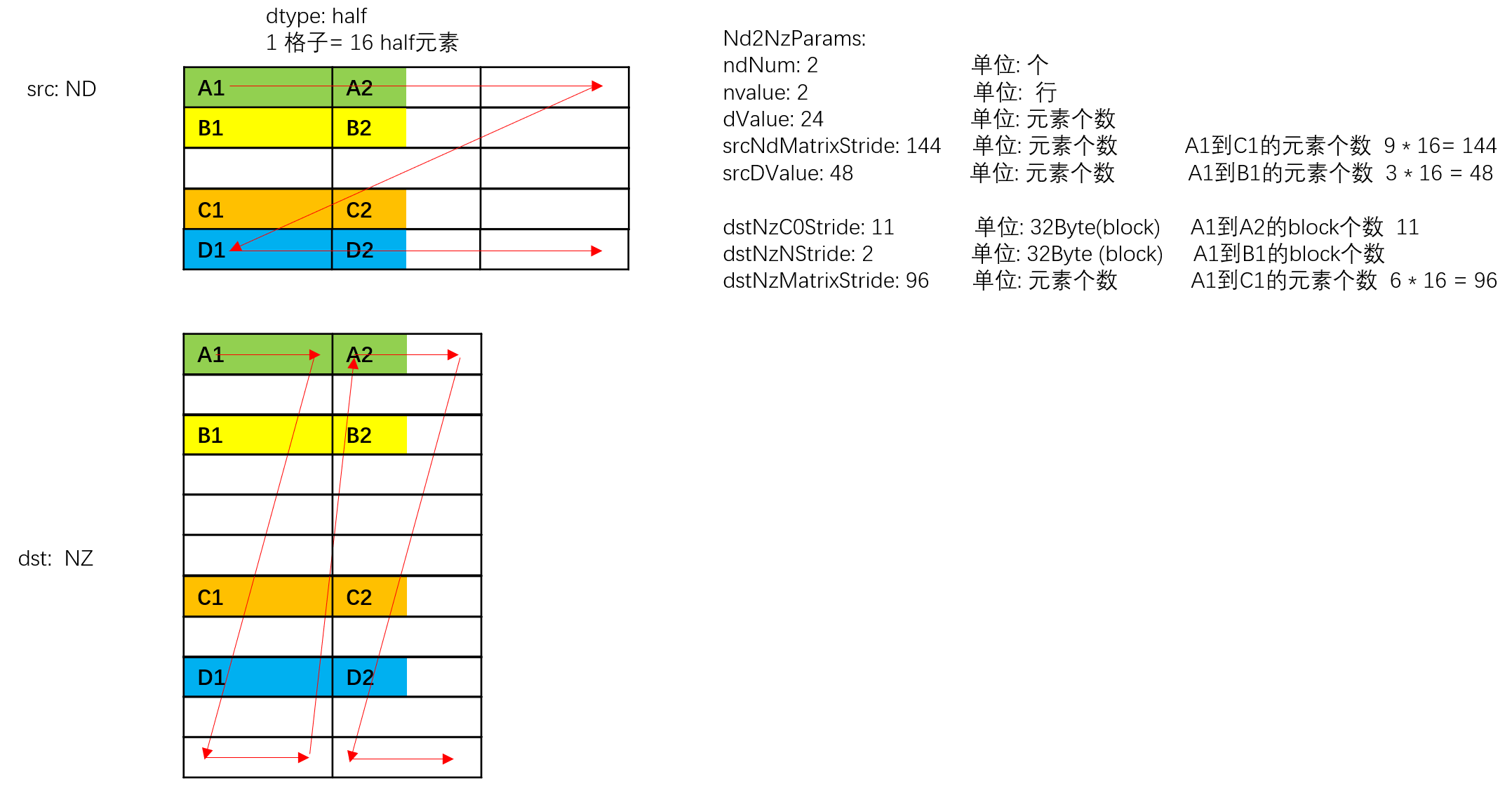
- Nz2NdParamsFull参数解析
表8 Nz2NdParamsFull 结构体内参数定义 参数名称
含义
ndNum
传输nz矩阵的数目,取值范围:ndNum∈[0, 4095]。
nValue
nz矩阵的行数,取值范围:nValue∈[1, 8192]。
dValue
nz矩阵的列数,取值范围:dValue∈[1, 8192]。dValue必须为16的倍数。
srcNdMatrixStride
源相邻nz矩阵的偏移(头与头),取值范围:srcNdMatrixStride∈[1, 512],单位256 (16 * 16) 个元素。
srcNStride
源同一nz矩阵的相邻z排布的偏移(头与头),取值范围:srcNStride∈[0, 4096],单位16个元素。
dstDStride
目的nd矩阵的相邻行的偏移(头与头),取值范围:dstDStride∈[1, 65535],单位:element。
dstNdMatrixStride
目的nd矩阵中,来自源相邻nz矩阵的偏移(头与头),取值范围:dstNdMatrixStride∈[1, 65535],单位:element。
以half数据类型为例,NZ2ND转换示意图如下,样例中参数设置值和解释说明如下:
- ndNum = 2,表示源nz矩阵的数目为2 (nz矩阵1为A1~A4 + B1~B4, nz矩阵2为C1~C4 + D1~D4)。
- nValue = 4,nz矩阵的行数,也就是矩阵的高度为4。
- dValue = 32,nz矩阵的列数,也就是矩阵的宽度为32个元素。
- srcNdMatrixStride = 1,表达相邻NZ矩阵起始地址间的偏移,即为A1~C1的距离,即为256个元素(16个datablock * 16个元素per block)。
- srcNStride = 4, 表示同一个源NZ矩阵的相邻Z排布的偏移,即为A1到B1的距离,即为64个元素(4个datablock* 16元素per block)。
- dstDStride = 160,表达一个目的ND矩阵的相邻行之间的偏移,即A1和A2之间的距离,即为10个datablock,即10 * 16 = 160个元素。
- dstNdMatrixStride = 48,表达dst中第x个目的ND矩阵的起点和第x+1个目的ND矩阵的起点的偏移,即A1和C1之间的距离,即为3个datablock, 3 * 16 = 48个元素。
图2 Nz2ND转换示意图(half数据类型)
以float数据类型为例,NZ2ND转换示意图如下,样例中参数设置值和解释说明如下:
- ndNum = 2,表示源nz矩阵的数目为2 (nz矩阵1为A1~A8 + B1~B8, nz矩阵2为C1~C8 + D1~D8)。
- nValue = 4,nz矩阵的行数,也就是矩阵的高度为4。
- dValue = 32,nz矩阵的列数,也就是矩阵的宽度为32个元素。
- srcNdMatrixStride = 1,表达相邻NZ矩阵起始地址间的偏移,即为A1到C1的距离,即为256个元素(32个datablock * 8元素per block)
- srcNStride = 4, 表示同一个源NZ矩阵的相邻Z排布的偏移,即为A1到B1的距离,即为64个元素 (8个datablock * 8元素per block)。
- dstDStride = 144,表达一个目的ND矩阵的相邻行之间的偏移,即A1和A3之间的距离,即为18个datablock,即18 * 8 = 144个元素。
- dstNdMatrixStride = 40,表达dst中第x个目的ND矩阵的起点和第x+1个目的ND矩阵的起点的偏移,即A1和C1之间的距离,即为5个datablock, 5 * 8 = 40个元素。
图3 Nz2ND转换示意图(float数据类型)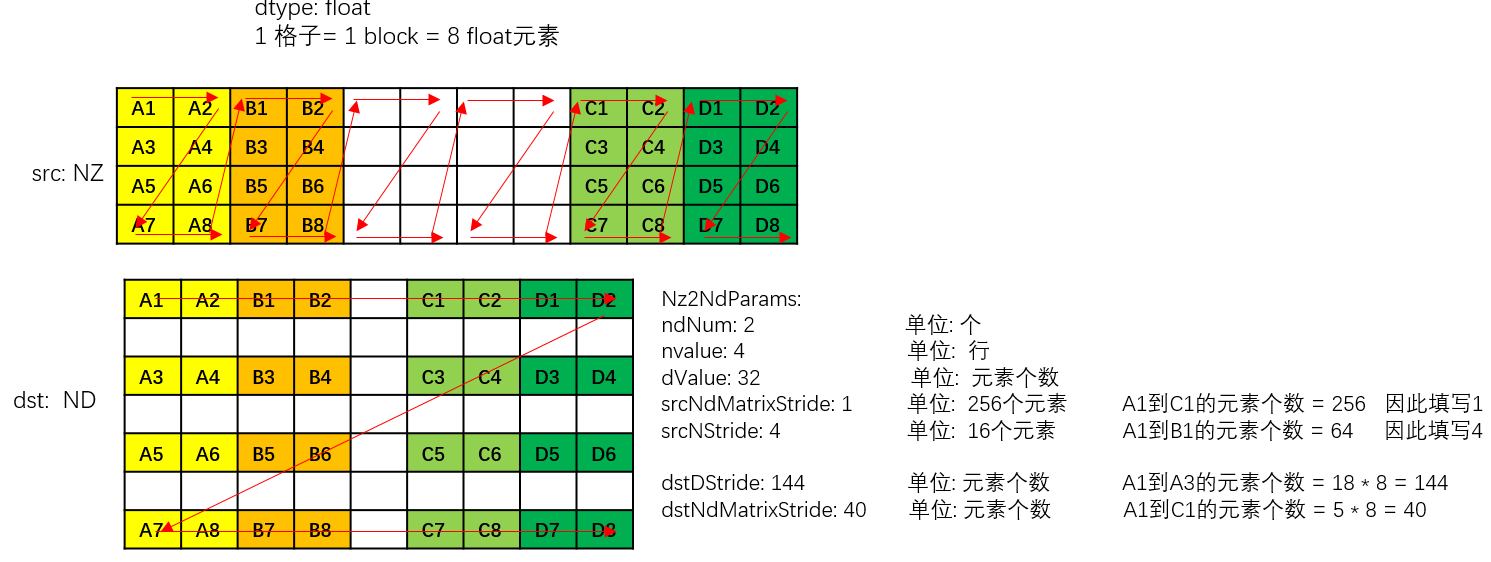
- DataCopyCO12DstParams
下文中的C0取值:一般情况下,C0=16;channelSplit(channel切分)使能时,C0=8。
表9 DataCopyCO12DstParams结构体参数定义 参数名称
含义
nSize
srcLocal横向方向的size大小。
- 不使能NZ2ND功能,必须为C0的倍数,此时连续传输数据块的个数为nSize/C0。
- 使能NZ2ND功能,不受限制。
mSize
srcLocal纵向方向的size大小。
dstStride
srcStride
quantPre
类型为QuantMode_t,默认值为QuantMode_t::NoQuant,即不使能量化功能。
QuantMode_t是一个枚举类型,用以控制量化模式,具体定义为:enum QuantMode_t { NoQuant, // 不使能量化功能 F322F16, // float量化成half F322BF16, // float量化成bfloat16_t DEQF16, // int32_t量化成half, scalar量化 VDEQF16, // int32_t量化成half,tensor量化 QF322B8_PRE, // float量化成int8_t/uint8_t,scalar量化 VQF322B8_PRE, // float量化成int8_t/uint8_t,tensor量化 REQ8, // int32_t量化成int8_t/uint8_t,tensor量化 VREQ8, // int32_t量化成int8_t/uint8_t,tensor量化 };reluPre
类型为uint8_t,配置relu操作的模式。
- 0:不使能relu
- 1:Normal relu
- 2:Leaky relu
channelSplit
类型为bool,配置是否使能channel切分,对于float类型的dstLocal生效。
- false:不使能
- true:使能
nz2ndEn
类型为bool,配置是否使能NZ2ND的格式转换,仅在L0C->GM通路生效。
如果要使能NZ2ND的功能需要同步调用SetFixpipeNz2ndFlag来设置格式转换的相关配置信息。
- false:不使能
- true:使能
支持的型号
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
调用示例
- 随路格式转换数据搬运,nz2nd
#include "kernel_operator.h" namespace AscendC { class KernelDataCopyUb2GmNz2Nd { public: __aicore__ inline KernelDataCopyUb2GmNz2Nd() {} __aicore__ inline void Init(__gm__ uint8_t* dstGm, __gm__ uint8_t* srcGm) { Nz2NdParamsFull intriParamsIn{1, 32, 32, 1, 32, 32, 1}; intriParams = intriParamsIn; srcGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ half *)srcGm); dstGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ half *)dstGm); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueSrcVecIn, 1, intriParams.nValue * intriParams.dValue * sizeof(half)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueSrcVecOut, 1, intriParams.nValue * intriParams.dValue * sizeof(half)); } __aicore__ inline void Process() { CopyIn(); Compute(); CopyOut(); } private: __aicore__ inline void CopyIn() { LocalTensor<half> srcLocal = inQueueSrcVecIn.AllocTensor<half>(); DataCopy(srcLocal, srcGlobal, intriParams.nValue * intriParams.dValue); inQueueSrcVecIn.EnQue(srcLocal); } __aicore__ inline void Compute() { LocalTensor<half> dstLocal = inQueueSrcVecIn.DeQue<half>(); LocalTensor<half> srcOutLocal = inQueueSrcVecOut.AllocTensor<half>(); DataCopy(srcOutLocal, dstLocal, intriParams.nValue * intriParams.dValue); inQueueSrcVecOut.EnQue(srcOutLocal); inQueueSrcVecIn.FreeTensor(dstLocal); } __aicore__ inline void CopyOut() { LocalTensor<half> srcOutLocalDe = inQueueSrcVecOut.DeQue<half>(); DataCopy(dstGlobal, srcOutLocalDe, intriParams); inQueueSrcVecOut.FreeTensor(srcOutLocalDe); } private: TPipe pipe; TQue<QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueSrcVecIn; TQue<QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> inQueueSrcVecOut; GlobalTensor<half> srcGlobal; GlobalTensor<half> dstGlobal; Nz2NdParamsFull intriParams; }; } // namespace AscendC extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void kernel_data_copy_nz2nd_ub2out(__gm__ uint8_t* src_gm, __gm__ uint8_t* dst_gm) { AscendC::KernelDataCopyUb2GmNz2Nd op; op.Init(dst_gm, src_gm); op.Process(); }结果示例:
输入数据(srcGlobal): [1 2 3 ... 1024] 输出数据(dstGlobal):[1 2 ... 15 16 513 514 ... 527 528 17 18 ... 31 32 529 530 ... 543 544 ...497 498 ... 511 512 1009 1010... 1023 1024]
- 随路格式转换数据搬运,通路:CO1->A1、CO1->GM
示例:mmad含有矩阵乘偏置,左矩阵和右矩阵的数据类型为int8_t,结果矩阵的数据类型为int32_t。量化模式DEQF16, scalar 量化参数为0.5,将mmad计算出的结果由int32_t量化成half并搬出。
#ifdef ASCENDC_CPU_DEBUG #include "tikicpulib.h" #endif #include "kernel_operator.h" #include "../../instrs/common_utils/register_utils.h" using namespace AscendC; SET_G_CORE_TYPE_IS_AIC namespace AscendC { template <typename dst_T, typename fmap_T, typename weight_T, typename dstCO1_T> class KernelCubeDataCopy{ public: __aicore__ inline KernelCubeDataCopy(uint16_t CoutIn, uint8_t dilationHIn, uint8_t dilationWIn, QuantMode_t deqModeIn) { // ceiling of 16 Cout = CoutIn; dilationH = dilationHIn; dilationW = dilationWIn; C0 = 32 / sizeof(fmap_T); C1 = channelSize / C0; coutBlocks = (Cout + 16 - 1) / 16; ho = H - dilationH * (Kh - 1); wo = W - dilationW * (Kw - 1); howo = ho * wo; howoRound = ((howo + 16 - 1) / 16) * 16; featureMapA1Size = C1 * H * W * C0; // shape: [C1, H, W, C0] weightA1Size = C1 * Kh * Kw * Cout * C0; // shape: [C1, Kh, Kw, Cout, C0] featureMapA2Size = howoRound * (C1 * Kh * Kw * C0); weightB2Size = (C1 * Kh * Kw * C0) * coutBlocks * 16; m = howo; k = C1 * Kh * Kw * C0; n = Cout; biasSize = Cout; // shape: [Cout] dstSize = coutBlocks * howo * 16; // shape: [coutBlocks, howo, 16] dstCO1Size = coutBlocks * howoRound * 16; fmRepeat = featureMapA2Size / (16 * C0); weRepeat = weightB2Size / (16 * C0); deqMode = deqModeIn; } __aicore__ inline void Init(__gm__ uint8_t* fmGm, __gm__ uint8_t* weGm, __gm__ uint8_t* biasGm, __gm__ uint8_t* deqGm, __gm__ uint8_t* dstGm) { fmGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ fmap_T*)fmGm); weGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ weight_T*)weGm); biasGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dstCO1_T*)biasGm); deqGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ uint64_t*)deqGm); dstGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dst_T*)dstGm); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueFmA1, 1, featureMapA1Size * sizeof(fmap_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueFmA2, 1, featureMapA2Size * sizeof(fmap_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueWeB1, 1, weightA1Size * sizeof(weight_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueWeB2, 1, weightB2Size * sizeof(weight_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueBiasA1, 1, biasSize * sizeof(dstCO1_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueDeqA1, 1, dstCO1Size * sizeof(uint64_t)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueDeqFB, 1, dstCO1Size * sizeof(uint64_t)); pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueCO1, 1, dstCO1Size * sizeof(dstCO1_T)); pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueA1, 1, dstCO1Size * sizeof(dst_T)); } __aicore__ inline void Process() { CopyIn(); Split(); Compute(); CopyOut(); } private: __aicore__ inline void CopyIn() { LocalTensor<fmap_T> featureMapA1 = inQueueFmA1.AllocTensor<fmap_T>(); LocalTensor<weight_T> weightB1 = inQueueWeB1.AllocTensor<weight_T>(); LocalTensor<dstCO1_T> biasA1 = inQueueBiasA1.AllocTensor<dstCO1_T>(); DataCopy(featureMapA1, fmGlobal, { 1, static_cast<uint16_t>(featureMapA1Size * sizeof(fmap_T) / 32), 0, 0 }); DataCopy(weightB1, weGlobal, { 1, static_cast<uint16_t>(weightA1Size * sizeof(weight_T) / 32), 0, 0 }); DataCopy(biasA1, biasGlobal, { 1, static_cast<uint16_t>(biasSize * sizeof(dstCO1_T) / 32), 0, 0 }); inQueueFmA1.EnQue(featureMapA1); inQueueWeB1.EnQue(weightB1); inQueueBiasA1.EnQue(biasA1); } __aicore__ inline void Split() { LocalTensor<fmap_T> featureMapA1 = inQueueFmA1.DeQue<fmap_T>(); LocalTensor<weight_T> weightB1 = inQueueWeB1.DeQue<weight_T>(); LocalTensor<fmap_T> featureMapA2 = inQueueFmA2.AllocTensor<fmap_T>(); LocalTensor<weight_T> weightB2 = inQueueWeB2.AllocTensor<weight_T>(); uint8_t padList[kPadSize] = {0, 0, 0, 0}; // load3dv2 LoadData(featureMapA2, featureMapA1, { padList, H, W, channelSize, k, howoRound, 0, 0, 1, 1, Kw, Kh, dilationW, dilationH, false, false, 0 }); // load2d LoadData(weightB2, weightB1, { 0, weRepeat, 1, 0, 0, false, 0 }); inQueueFmA2.EnQue<fmap_T>(featureMapA2); inQueueWeB2.EnQue<weight_T>(weightB2); inQueueFmA1.FreeTensor(featureMapA1); inQueueWeB1.FreeTensor(weightB1); } __aicore__ inline void Compute() { LocalTensor<fmap_T> featureMapA2 = inQueueFmA2.DeQue<fmap_T>(); LocalTensor<weight_T> weightB2 = inQueueWeB2.DeQue<weight_T>(); LocalTensor<dstCO1_T> dstCO1 = outQueueCO1.AllocTensor<dstCO1_T>(); LocalTensor<dstCO1_T> biasA1 = inQueueBiasA1.DeQue<dstCO1_T>(); // C = A * B + bias // m: 左矩阵Height, k: 左矩阵Width, n: 右矩阵Width Mmad(dstCO1, featureMapA2, weightB2, biasA1, { m, n, k, true, 0, false, false, false }); outQueueCO1.EnQue<dstCO1_T>(dstCO1); inQueueFmA2.FreeTensor(featureMapA2); inQueueWeB2.FreeTensor(weightB2); } __aicore__ inline void CopyOut() { LocalTensor<dstCO1_T> dstCO1 = outQueueCO1.DeQue<dstCO1_T>(); LocalTensor<dst_T> dstA1 = outQueueA1.DeQue<dst_T>(); // 使能DEQF16量化,量化参数设置为0.5 float tmp = (float)0.5; // 将float的tmp转换成uint64_t的deqScalar uint64_t deqScalar = static_cast<uint64_t>(*reinterpret_cast<int32_t*>(&tmp)); bool nz2ndEn = false; // nz2nd不使能时,nSize必须为16的倍数 uint16_t nSize = coutBlocks * 16; uint16_t mSize = m; // srcStride必须为16的倍数 uint16_t srcStride = (m + 16 - 1) / 16 * 16; // nz2nd不使能时,dstStride为burst头到头的距离,且为32B对齐 uint32_t dstStride = m * sizeof(dst_T) * 16 / 32; if (nz2ndEn) { // nd矩阵的数量为1,src_nd_stride与dst_nd_stride填0 SetFixpipeNz2ndFlag(1, 0, 0); // nz2nd使能时,nSize可以不为16的倍数,与Mmad的n保持一致 nSize = n; // nz2nd使能时,dstStride表示同一nd矩阵的相邻连续行的间隔,与n保持一致 dstStride = nSize; }; // 不使能relu与channelSplit DataCopyCO12DstParams intriParams(nSize, mSize, dstStride, srcStride, deqMode, 0, false, nz2ndEn); // mov l0c to gm, deq scalar quant SetFixpipePreQuantFlag(deqScalar); // 设置量化参数 PipeBarrier<PIPE_FIX>(); DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstCO1, intriParams); // // mov l0c to gm, deq tensor quant // // 需要额外申请deq tensor的gm空间,将值搬运到workA1 // LocalTensor<uint64_t> workA1 = inQueueDeqA1.DeQue<uint64_t>(); // // deq tensor的size // uint16_t deqSize = 128; // DataCopy(workA1, deqGlobal, deqSize); // // deq tensor在fix上的地址 // LocalTensor<uint64_t> deqFB = inQueueDeqFB.AllocTensor<uint64_t>(); // // l1->fix, burst_len unit is 128Bytes // uint16_t fbufBurstLen = deqSize / 128; // DataCopyParams dataCopyParams(1, fbufBurstLen, 0, 0); // DataCopy(deqFB, workA1, dataCopyParams); // // 设置量化tensor // SetFixPipeConfig(deqFB); // PipeBarrier<PIPE_FIX>(); // DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstCO1, intriParams); // inQueueDeqA1.FreeTensor(workA1); // inQueueDeqFB.FreeTensor(deqFB); // // mov l0c to l1, deq scalar quant, and then mov l1 to gm // SetFixpipePreQuantFlag(deqScalar); // 设置量化参数 // PipeBarrier<PIPE_FIX>(); // DataCopy(dstA1, dstCO1, intriParams); // DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstA1, dstCO1Size); // // mov l0c to l1, deq tensor quant, and then mov l1 to gm // LocalTensor<uint64_t> workA1 = inQueueDeqA1.DeQue<uint64_t>(); // uint16_t deqSize = 128; // DataCopy(workA1, deqGlobal, deqSize); // LocalTensor<uint64_t> deqFB = inQueueDeqFB.AllocTensor<uint64_t>(); // uint16_t fbufBurstLen = deqSize / 128; // DataCopyParams dataCopyParams(1, fbufBurstLen, 0, 0); // DataCopy(deqFB, workA1, dataCopyParams); // // 设置量化tensor // SetFixPipeConfig(deqFB); // PipeBarrier<PIPE_FIX>(); // DataCopy(dstA1, dstCO1, intriParams); // DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstA1, dstCO1Size); // inQueueDeqA1.FreeTensor(workA1); // inQueueDeqFB.FreeTensor(deqFB); // outQueueCO1.FreeTensor(dstCO1); // outQueueA1.FreeTensor(dstA1); } private: TPipe pipe; // feature map queue TQue<QuePosition::A1, 1> inQueueFmA1; TQue<QuePosition::A2, 1> inQueueFmA2; // weight queue TQue<QuePosition::B1, 1> inQueueWeB1; TQue<QuePosition::B2, 1> inQueueWeB2; // bias queue TQue<QuePosition::A1, 1> inQueueBiasA1; // deq tensor queue TQue<QuePosition::A1, 1> inQueueDeqA1; // fb dst of deq tensor TQue<QuePosition::C2PIPE2GM, 1> inQueueDeqFB; // dst queue TQue<QuePosition::CO1, 1> outQueueCO1; TQue<QuePosition::A1, 1> outQueueA1; GlobalTensor<fmap_T> fmGlobal; GlobalTensor<weight_T> weGlobal; GlobalTensor<dst_T> dstGlobal; GlobalTensor<uint64_t> deqGlobal; GlobalTensor<dstCO1_T> biasGlobal; uint16_t channelSize = 32; uint16_t H = 4, W = 4; uint8_t Kh = 2, Kw = 2; uint16_t Cout; uint16_t C0, C1; uint8_t dilationH, dilationW; uint16_t coutBlocks, ho, wo, howo, howoRound; uint32_t featureMapA1Size, weightA1Size, featureMapA2Size, weightB2Size, biasSize, dstSize, dstCO1Size; uint16_t m, k, n; uint8_t fmRepeat, weRepeat; uint8_t kPadSize = 4; QuantMode_t deqMode = QuantMode_t::NoQuant; }; } // namespace AscendC #define KERNEL_CUBE_DATACOPY(dst_type, fmap_type, weight_type, dstCO1_type, CoutIn, dilationHIn, dilationWIn, deqModeIn) \ extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void cube_datacopy_kernel_##fmap_type(__gm__ uint8_t* fmGm, __gm__ uint8_t* weGm, \ __gm__ uint8_t* biasGm, __gm__ uint8_t* deqGm, __gm__ uint8_t* dstGm) \ { \ if (g_coreType == AIV) { \ return; \ } \ AscendC::KernelCubeDataCopy<dst_type, fmap_type, weight_type, dstCO1_type> op(CoutIn, dilationHIn, dilationWIn, \ deqModeIn); \ op.Init(fmGm, weGm, biasGm, deqGm, dstGm); \ op.Process(); \ } KERNEL_CUBE_DATACOPY(half, int8_t, int8_t, int32_t, 128, 1, 1, QuantMode_t::DEQF16);